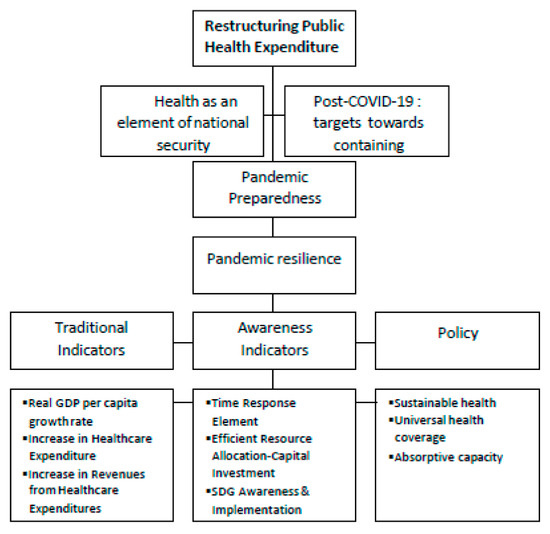
Proactive Preparedness: Navigating Pandemic Planning and Response
The importance of pandemic preparedness has been underscored by global events. In this article, we explore the significance of pandemic preparedness plans, the key elements they encompass, and their role in effective response strategies.
Understanding the Need for Preparedness
The unpredictability of pandemics makes proactive preparedness crucial. Understanding the potential impact of a pandemic and the rapid transmission of infectious diseases emphasizes the need for comprehensive plans to safeguard public health.
Key Elements of Pandemic Preparedness Plans
Effective pandemic preparedness plans incorporate various elements. These include early detection and surveillance systems, robust communication strategies, resource allocation, healthcare infrastructure readiness, and community engagement to ensure a holistic approach to mitigating the impact of a pandemic.
Early Detection and Surveillance Systems
Early detection is paramount in controlling the spread of infectious diseases. Surveillance systems that monitor trends in illness, laboratory testing, and data analysis enable authorities to identify and respond swiftly to potential outbreaks.
Robust Communication Strategies
Clear and transparent communication is essential during a pandemic. Preparedness plans should include strategies for disseminating accurate information to the public, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders. Timely communication helps build trust and ensures that individuals are well-informed about preventive measures and the evolving situation.
Resource Allocation and Stockpiling
Allocating resources efficiently is a critical aspect of pandemic preparedness. This includes stockpiling medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, personal protective equipment (PPE), and ensuring the availability of healthcare facilities and personnel to handle increased patient loads.
Healthcare Infrastructure Readiness
Preparedness plans must assess and enhance healthcare infrastructure readiness. This involves identifying surge capacity in hospitals, ensuring access to ventilators and other critical equipment, and establishing protocols for triage and patient care in the event of overwhelming demand.
Community Engagement and Education
Engaging communities in preparedness efforts is vital. Educational campaigns that inform the public about preventive measures, symptoms, and available resources empower individuals to take an active role in protecting themselves and others.
Global Collaboration and Cooperation
Pandemics transcend borders, necessitating global collaboration. Preparedness plans should emphasize international cooperation in information sharing, research, and resource allocation to ensure a coordinated response that addresses the interconnected nature of global health.
Response Coordination and Simulation Exercises
Regular coordination and simulation exercises are integral components of preparedness plans. These drills enable healthcare professionals, emergency responders, and public health agencies to practice and refine their response strategies, identifying areas for improvement and ensuring a coordinated and efficient reaction to an actual event.
Adaptability and Continuous Improvement
Preparedness plans must be adaptable and subject to continuous improvement. Regular evaluations, updates based on lessons learned from past events, and staying informed about emerging threats contribute to the agility needed to address evolving pandemic scenarios.
Pandemic Preparedness Plans: A Link to Comprehensive Health
To explore further insights and resources on pandemic preparedness plans, visit The Healthy Consumer – Pandemic Preparedness Plans. This platform provides valuable information and articles on navigating preparedness, ensuring that individuals and communities are equipped to respond effectively to the challenges posed by pandemics.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Public Health Through Preparedness
In conclusion, proactive pandemic preparedness is a cornerstone of safeguarding public health. Comprehensive plans that encompass early detection, communication, resource allocation, infrastructure readiness, community engagement, global collaboration, response coordination, and continuous improvement play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of pandemics and ensuring a resilient and responsive healthcare system.
