Navigating Pandemics: Effective Risk Management Strategies
Unraveling the Complexities of Pandemic Risk Management
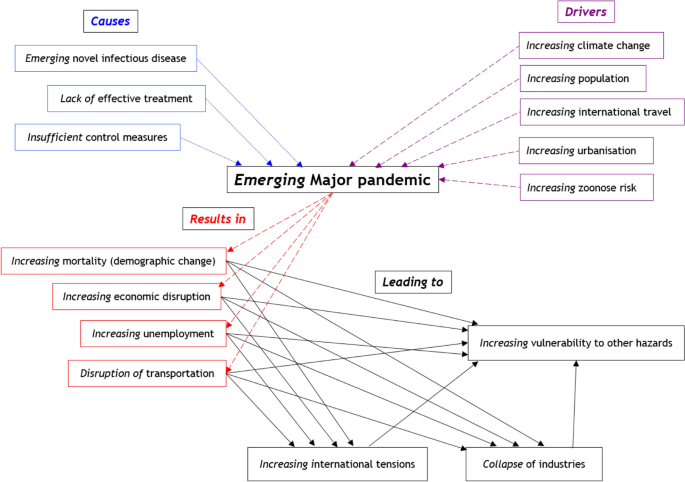
The emergence of a pandemic presents a multifaceted challenge that demands a strategic and comprehensive approach to risk management. As organizations grapple with the uncertainties brought about by global health crises, effective pandemic risk management becomes an indispensable tool in navigating the complexities of these unprecedented times.
Understanding the Dynamic Nature of Pandemic Risks
Pandemic risks are inherently dynamic, evolving with the progression of a health crisis. To effectively manage these risks, organizations must first understand the fluid nature of the threat. This involves continuous monitoring of global health data, staying abreast of emerging variants, and anticipating the potential impacts on various aspects of operations.
Proactive Preparedness: A Cornerstone of Risk Management
The old adage “prevention is better than cure” rings particularly true in the realm of pandemic risk management. Proactive preparedness involves establishing robust contingency plans, ensuring a resilient supply chain, and implementing measures to safeguard the health and well-being of employees. A well-prepared organization is better equipped to weather the challenges posed by a pandemic.
Data-Driven Decision-Making in Uncertain Times
In the face of a pandemic, data becomes a powerful ally in risk management. Analyzing epidemiological data, monitoring infection rates, and utilizing predictive modeling aid organizations in making informed decisions. Data-driven insights contribute to the development of effective strategies, ensuring a nimble and adaptive response to evolving circumstances.
Flexibility as a Key Component of Risk Mitigation
The ability to adapt and pivot swiftly is a hallmark of effective pandemic risk management. Organizations must embed flexibility into their operations, allowing for rapid adjustments to changing circumstances. This includes flexible work arrangements, adaptable supply chain strategies, and contingency plans that can be activated promptly in response to emerging risks.
Employee Well-Being as a Priority in Risk Mitigation
Managing pandemic risks extends beyond operational considerations to encompass the well-being of employees. Prioritizing mental health, providing support mechanisms, and fostering a culture of open communication contribute to a resilient workforce. A healthy and supported team is better equipped to navigate the challenges posed by a pandemic.
Supply Chain Resilience in the Face of Disruptions
Pandemics can disrupt supply chains on a global scale. Ensuring supply chain resilience involves diversifying suppliers, maintaining adequate inventory levels, and establishing alternative sourcing strategies. A resilient supply chain mitigates the impact of disruptions, ensuring continuity in operations even in the face of widespread challenges.
Scenario Planning for Contingency Preparedness
Effective pandemic risk management includes scenario planning to anticipate and prepare for a range of potential outcomes. This proactive approach allows organizations to identify vulnerabilities, assess the impact of various scenarios, and implement preemptive measures. Scenario planning enhances the organization’s ability to navigate uncertainties with agility and resilience.
Communication Strategies for Transparency and Assurance
Transparent communication is integral to pandemic risk management. Clear and timely communication fosters trust among employees, stakeholders, and the broader community. Providing regular updates, addressing concerns openly, and ensuring accessibility to accurate information contribute to a cohesive and informed response to the risks posed by a pandemic.
Continuous Evaluation and Learning for Future Preparedness
The culmination of effective pandemic risk management involves continuous evaluation and learning. After navigating a crisis, organizations must reflect on their responses, identify areas for improvement, and integrate lessons learned into future risk management strategies. This iterative process enhances an organization’s overall resilience and preparedness for future pandemics.
To delve deeper into the intricacies of pandemic risk management, visit Pandemic Risk Management. As organizations confront the challenges of global health crises, a proactive and adaptive approach to risk management becomes a cornerstone of resilience. By understanding the dynamic nature of pandemic risks and implementing comprehensive strategies, organizations can not only navigate current crises but also fortify themselves for the uncertainties of the future.
Remote Evolution: Adapting Work in the Pandemic

The Swift Transition: Remote Work in the Pandemic Era
The onset of the global pandemic necessitated a rapid shift in work dynamics, leading to the widespread adoption of remote work. This abrupt transition prompted organizations worldwide to rethink and adapt their strategies to accommodate a remote workforce. The agility with which businesses adapted to this new normal became a testament to resilience in the face of unprecedented challenges.
Technological Overhaul: Enabling Seamless Connectivity
Central to the success of remote work adaptations was a technological overhaul. Organizations invested in robust digital infrastructure, collaboration tools, and secure communication platforms. This technological leap was essential for creating an environment where employees could seamlessly connect, collaborate, and maintain productivity, regardless of physical locations.
Flexibility Redefined: Embracing Remote Work Structures
Adapting to remote work required a redefinition of traditional notions of flexibility. Remote work adaptations went beyond merely allowing employees to work from home; they involved a shift in mindset and the establishment of flexible work structures. Organizations embraced results-driven approaches, focusing on outcomes rather than rigid working hours, fostering a culture of trust and autonomy.
Employee Well-Being: Prioritizing Mental Health and Work-Life Balance
As the remote work landscape evolved, organizations recognized the importance of prioritizing employee well-being. Remote work adaptations extended beyond professional aspects to consider the mental health and work-life balance of employees. Initiatives such as virtual wellness programs, flexible schedules, and clear communication channels aimed to support employees in maintaining a healthy work-life integration.
Collaborative Culture: Nurturing Connection in a Virtual World
Maintaining a sense of connection and collaboration became pivotal in remote work adaptations. Organizations actively fostered a collaborative culture through virtual team-building activities, regular video meetings, and digital collaboration platforms. These initiatives aimed to recreate the camaraderie of an in-person workplace and mitigate the potential feelings of isolation among remote team members.
Security Imperative: Safeguarding Digital Workspaces
With the shift to remote work, ensuring the security of digital workspaces became a paramount concern. Organizations implemented robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive data and protect against potential cyber threats. This adaptation involved not only technological solutions but also comprehensive training programs to educate employees on best practices for maintaining a secure remote work environment.
Adaptive Leadership: Guiding Teams through Uncertainty
Adapting to remote work required adaptive leadership that could guide teams through the uncertainty of the pandemic. Leaders embraced a more empathetic and communicative approach, recognizing the unique challenges faced by remote team members. Transparent communication, regular check-ins, and responsive leadership became essential components of remote work adaptations.
Continuous Learning: Upskilling for a Digital Future
Recognizing the digital shift as a long-term transformation, organizations prioritized continuous learning and upskilling initiatives. Remote work adaptations meant equipping employees with the necessary digital skills to thrive in a virtual environment. Online training programs, virtual workshops, and mentorship opportunities became integral to building a workforce prepared for the challenges of a digital future.
Agile Policies: Embracing Change for Ongoing Success
Successful remote work adaptations were characterized by organizations embracing agile policies that could evolve with changing circumstances. The ability to adapt policies and practices in response to feedback, technological advancements, and emerging trends ensured ongoing success in the remote work landscape. Flexibility in policies became a cornerstone for sustaining productivity and employee satisfaction.
Future of Work: Shaping a Hybrid Landscape
As organizations navigated the challenges of remote work adaptations, they began envisioning a future of work that embraced a hybrid model. The experiences gained during the pandemic informed strategies for creating a flexible work environment that combines the benefits of remote work with in-person collaboration. This hybrid landscape aims to provide employees with choices that suit their individual preferences and the needs of the organization.
To explore more about remote work adaptations, visit Remote Work Pandemic Adaptations. The journey of adapting to remote work during the pandemic has been transformative, pushing organizations to reconsider their structures and strategies. The lessons learned from these adaptations will likely shape the future of work, creating a more flexible, technology-enabled, and people-centric work environment.
Strategic Readiness: Pandemic Preparedness Training
Strategic Readiness: Pandemic Preparedness Training
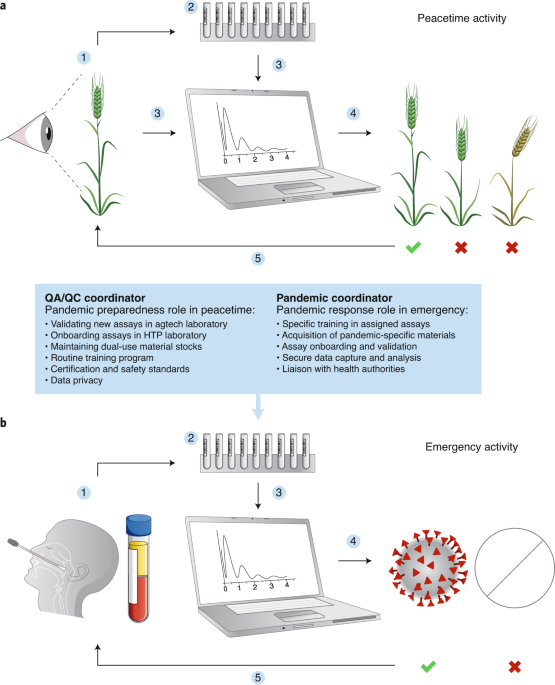
In the face of global health crises, pandemic preparedness training has emerged as a critical component in ensuring the resilience and adaptability of individuals, organizations, and communities. This comprehensive training equips participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate and respond effectively to pandemics.
Understanding the Importance of Preparedness:
The first step in pandemic preparedness training is understanding the importance of being prepared. This section delves into the reasons why preparedness is crucial, emphasizing the unpredictable nature of pandemics and the potential impact on individuals, businesses, and public health systems.
Pandemic Preparedness Training: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on pandemic preparedness training, visit Pandemic Preparedness Training for valuable insights and resources.
Risk Assessment and Planning:
Pandemic preparedness begins with a thorough risk assessment and planning process. This includes identifying potential risks, assessing vulnerabilities, and developing comprehensive plans to mitigate the impact of a pandemic. Participants learn how to create tailored strategies based on their specific context, ensuring a proactive rather than reactive approach.
Health and Safety Protocols:
A crucial aspect of pandemic preparedness training is the understanding and implementation of health and safety protocols. This involves educating participants on proper hygiene practices, the effective use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to public health guidelines. These protocols not only protect individuals but also contribute to broader community well-being.
Communication Strategies in Crisis:
Effective communication is paramount during a pandemic. This section focuses on training participants in communication strategies tailored for crisis situations. From internal communication within organizations to transparent and timely information dissemination to the public, these strategies help maintain trust and facilitate a coordinated response.
Role-Specific Training for Professionals:
Different professions require specific skills and knowledge in pandemic situations. This part of the training tailors information for various professionals, such as healthcare workers, emergency responders, and business leaders. Role-specific training ensures that each sector is well-prepared to fulfill its unique responsibilities during a pandemic.
Utilizing Technology for Preparedness:
In the digital age, technology plays a crucial role in pandemic preparedness. This segment explores the use of technology for early detection, monitoring, and communication. From surveillance systems to data analytics, participants learn how technology can enhance the effectiveness of pandemic response efforts.
Community Engagement and Support:
Community engagement is a cornerstone of effective pandemic preparedness. Training emphasizes the importance of community involvement, collaboration, and support networks. Participants learn how to engage with diverse communities, address concerns, and foster a sense of collective responsibility for health and well-being.
Simulations and Drills:
Hands-on experience is invaluable in pandemic preparedness training. Simulations and drills allow participants to apply their knowledge in realistic scenarios, honing their decision-making skills and teamwork. These exercises provide a practical understanding of the challenges posed by pandemics and enhance overall readiness.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
Pandemic preparedness is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning and adaptation. This section of the training focuses on creating a culture of preparedness, encouraging participants to stay informed, update plans regularly, and remain agile in the face of evolving health challenges.
Conclusion:
Pandemic preparedness training is not just a precautionary measure; it is a strategic investment in the resilience and well-being of individuals and communities. By understanding the importance of preparedness, conducting risk assessments, implementing health and safety protocols, fostering effective communication, providing role-specific training, leveraging technology, engaging with communities, and conducting simulations, participants are better equipped to navigate the complexities of pandemics. This comprehensive training sets the stage for a proactive and coordinated response, ensuring that individuals and organizations are strategically ready to face the challenges of global health crises.
Building Resilience: Strategies for Navigating the Pandemic

Navigating Uncertainty: Pandemic Resilience Strategies
In the face of a global pandemic, cultivating resilience is paramount. This article delves into effective strategies for building and maintaining resilience, providing individuals and communities with the tools to navigate uncertainty and emerge stronger.
Understanding the Dynamics of Resilience
Resilience is more than just bouncing back; it’s about adapting, learning, and thriving in the face of adversity. Understanding the dynamics of resilience is the first step in developing strategies that go beyond mere survival and foster growth even in challenging times.
Cultivating a Positive Mindset
A positive mindset forms the bedrock of resilience. Cultivating optimism, focusing on strengths, and reframing challenges as opportunities contribute to a mindset that can weather the storm. Positivity is a powerful force that propels individuals forward even when faced with adversity.
Building a Supportive Social Network
Social connections are instrumental in resilience. Building a supportive social network provides a foundation of strength. Whether through family, friends, or community, having a network that fosters mutual support and encouragement enhances an individual’s ability to cope with challenges.
Prioritizing Emotional Well-being
Emotional well-being is a cornerstone of resilience. Prioritizing mental health, managing stress, and seeking professional support when needed contribute to emotional resilience. Strategies such as mindfulness, meditation, and self-care rituals play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy emotional balance.
Developing Adaptive Coping Strategies
Adaptive coping strategies involve the ability to adjust and respond effectively to challenges. Developing a repertoire of coping mechanisms, both practical and emotional, equips individuals to navigate the uncertainties of a pandemic. Flexibility and adaptability become key components of resilience.
Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
Setting realistic goals and expectations is pivotal in resilience. Establishing achievable milestones and acknowledging incremental progress fosters a sense of control and accomplishment. This approach prevents feelings of overwhelm and contributes to a more positive outlook.
Fostering Continuous Learning and Growth
Resilience is closely tied to continuous learning and growth. Embracing challenges as opportunities for personal and professional development fosters resilience. A mindset that sees setbacks as stepping stones to growth encourages individuals to adapt and thrive in ever-changing circumstances.
Promoting Physical Health and Well-being
Physical health is intertwined with resilience. Prioritizing a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep, enhances overall well-being. A robust physical foundation supports individuals in facing the physical and mental demands of challenging times.
Establishing Crisis Preparedness Plans
Proactive crisis preparedness is an integral resilience strategy. Establishing plans that outline responses to potential challenges, whether personal or community-wide, provides a roadmap for action. Preparedness plans instill a sense of readiness and empowerment in the face of uncertainty.
Cultivating a Sense of Purpose and Meaning
A sense of purpose and meaning anchors resilience. Understanding one’s values and aligning actions with a greater purpose provides motivation and direction. Cultivating a sense of meaning in daily activities contributes to a resilient mindset that transcends the immediate challenges.
Explore Pandemic Resilience Strategies
Explore further insights and strategies for building resilience during a pandemic at Pandemic Resilience Strategies. By adopting and adapting these strategies, individuals can fortify their resilience, not just to endure the storm, but to emerge stronger on the other side.




