World in Crisis: Navigating the Global Emergency Pandemic

Unprecedented Challenges Unveiled: Global Emergency Pandemic
The world finds itself grappling with an unprecedented global emergency pandemic, a crisis that transcends borders and touches every facet of our existence. As we navigate these uncharted waters, it becomes essential to dissect the multifaceted challenges posed by this global health crisis and explore the innovative strategies employed in response.
Understanding the Global Impact
The impact of a global emergency pandemic is profound and all-encompassing. Beyond the immediate health threats, economies stagger, social structures strain, and daily life undergoes a seismic shift. Understanding the comprehensive impact is crucial for crafting effective strategies that address not only the health aspects but also the broader implications of the crisis.
The Role of International Collaboration
In the face of a global emergency, collaboration on an international scale becomes imperative. Nations, organizations, and individuals must unite their efforts to share knowledge, resources, and support. International collaboration not only aids in addressing immediate challenges but also lays the foundation for a more resilient and interconnected global community.
Public Health Measures: A Global Imperative
Amidst a global emergency pandemic, public health measures emerge as a frontline defense. From widespread testing and contact tracing to vaccination campaigns, nations worldwide implement measures to curb the spread of the virus. The effectiveness of these measures relies heavily on communication, coordination, and adherence on a global scale.
Technology’s Crucial Role in Crisis Management
Technology assumes a pivotal role in managing a global emergency. From tracking the spread of the virus to facilitating remote work and virtual healthcare, technological innovations have proven instrumental. Harnessing the power of data, artificial intelligence, and communication technologies is key to crafting agile and effective responses in a rapidly evolving crisis.
Adapting Education for a Changing World
Education systems face unique challenges during a global emergency pandemic. School closures, remote learning, and adapting curricula to address the crisis become paramount. Innovations in digital education, virtual classrooms, and inclusive approaches ensure that the continuity of education remains a priority even amidst the disruptions caused by the global health emergency.
Economic Resilience and Recovery Strategies
The economic fallout from a global emergency is significant. Governments and businesses grapple with downturns, job losses, and disruptions to supply chains. Crafting resilient economic strategies and recovery plans becomes essential to mitigate the long-term impact and foster sustainable growth in the aftermath of the pandemic.
Social Implications and Mental Health Considerations
Beyond the physical health implications, a global emergency pandemic takes a toll on mental health and social well-being. Social isolation, anxiety, and uncertainty become pervasive challenges. Prioritizing mental health support and fostering community resilience are crucial components of a holistic response to the social implications of the crisis.
Environmental Considerations in Crisis Response
The global emergency pandemic also sheds light on the interconnectedness of health and the environment. From the impact of human activity on the emergence of zoonotic diseases to the environmental benefits observed during lockdowns, the crisis prompts a reevaluation of our relationship with the planet and the need for sustainable practices.
Looking Ahead: Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness
As the world grapples with the global emergency pandemic, the importance of learning from the crisis becomes evident. Analyzing response strategies, identifying shortcomings, and implementing lessons learned are crucial for future preparedness. The ability to adapt, innovate, and collaborate globally will define our readiness for the challenges that lie ahead.
To delve deeper into the complexities of navigating a global emergency pandemic, explore Global Emergency Pandemic. As we confront this unparalleled challenge, it is through collective effort, innovation, and global solidarity that we can pave the way for a healthier and more resilient future.
Remote Work Revolution: Navigating the Pandemic Shift

Introduction
The pandemic has catalyzed a significant shift in work dynamics, ushering in the era of remote work. This article delves into the transformative impact of remote work during the pandemic, exploring its challenges, benefits, and the lasting changes it has brought to the traditional work landscape.
The Acceleration of Remote Work Adoption
Remote work, once a limited practice, experienced a rapid acceleration during the pandemic. With lockdowns and safety concerns, organizations worldwide swiftly embraced remote work as a viable solution to ensure business continuity. This sudden shift led to a reevaluation of traditional work structures and a reimagining of how work could be accomplished.
Challenges of Remote Work
Despite its widespread adoption, remote work posed several challenges. The abrupt transition left many unprepared for the technical and psychological aspects of working from home. Issues such as inadequate home office setups, the blurring of work-life boundaries, and feelings of isolation became prevalent challenges that both employees and employers had to navigate.
Technology as the Enabler
Technology emerged as the linchpin that enabled the remote work revolution. Video conferencing, collaboration tools, and cloud-based platforms became essential in facilitating communication and project collaboration. The pandemic underscored the importance of investing in robust technology infrastructure to support remote work seamlessly.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
One of the notable benefits of remote work during the pandemic was the newfound flexibility it provided. Employees gained the ability to tailor their work schedules to accommodate personal needs, fostering a better work-life balance. This flexibility became a crucial factor in maintaining employee well-being and job satisfaction.
Impact on Corporate Culture
The shift to remote work prompted organizations to reevaluate their corporate culture. Maintaining a sense of connection and camaraderie among remote teams became a priority. Companies implemented virtual team-building activities, online social events, and communication strategies to nurture a positive and inclusive remote work culture.
Cost Savings and Productivity Gains
Remote work also brought about cost savings for both employees and employers. Reduced commuting expenses, lower overhead costs for office maintenance, and the potential for accessing a global talent pool contributed to financial advantages. Many organizations reported increases in productivity, challenging preconceptions about the effectiveness of remote work.
Addressing Mental Health Concerns
While remote work offered flexibility, it also raised concerns about mental health. The isolation and blurred boundaries between work and personal life took a toll on many individuals. Organizations began implementing mental health initiatives, offering resources and support to help employees cope with the challenges posed by remote work.
Navigating Remote Team Collaboration
Effective collaboration within remote teams became a focal point for organizations. Strategies for virtual teamwork, project management, and clear communication channels were crucial in ensuring that teams remained cohesive and productive. The pandemic prompted the exploration of innovative tools and methodologies to enhance remote collaboration.
The Hybrid Work Model
As the pandemic evolved, organizations started considering hybrid work models that blend remote and in-office work. This approach aims to combine the benefits of remote work, such as flexibility, with the advantages of in-person collaboration. The hybrid model reflects a nuanced understanding of diverse employee preferences and the evolving nature of work.
Future of Remote Work
The pandemic has undoubtedly reshaped the future of work, with remote work likely to remain a significant component. The lessons learned during this transformative period will influence how organizations approach work arrangements, technology integration, and employee well-being in the post-pandemic era.
Conclusion with Link
In conclusion, the remote work revolution sparked by the pandemic has redefined the landscape of work. For further insights into navigating the challenges and embracing the opportunities of remote work, visit The Healthy Consumer website. Explore the future of work and adapt to the changing dynamics.
Nurturing Mental Wellbeing During the Pandemic Challenges

Navigating the Challenges: Nurturing Mental Wellbeing During the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought forth unprecedented challenges, impacting every facet of life. Amidst the physical health concerns, the pandemic has also triggered a global mental health crisis. Nurturing mental wellbeing during these challenging times has become a paramount concern, requiring a holistic approach to address the multifaceted aspects of mental health.
Understanding the Impact on Mental Health
The uncertainties, social isolation, economic pressures, and health anxieties associated with the pandemic have collectively contributed to a surge in mental health issues. Understanding the impact of these stressors on mental health is the first step towards implementing effective strategies for support and resilience.
Prioritizing Self-Care and Routine
Amid the chaos, establishing and maintaining a routine is crucial for mental wellbeing. Prioritizing self-care activities, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and healthy eating, can significantly contribute to stress reduction and emotional balance. Small, consistent self-care practices become pillars of stability in uncertain times.
Fostering Social Connections in a Distanced World
Social distancing measures have led to increased feelings of isolation and loneliness. Fostering social connections, even in a virtual space, is essential for mental wellbeing. Regular video calls, online group activities, and staying connected with friends and family can provide a sense of support and combat feelings of loneliness.
Seeking Professional Support
For individuals facing more severe mental health challenges, seeking professional support is crucial. Therapists, counselors, and mental health professionals can provide valuable guidance and therapeutic interventions. Telehealth services have become more widely available, offering convenient and accessible options for seeking help.
Addressing Pandemic-Related Anxiety
The constant barrage of pandemic-related information can contribute to heightened anxiety levels. Implementing strategies to manage and limit exposure to news, fact-checking information sources, and focusing on positive and uplifting content can help mitigate pandemic-related anxiety.
Encouraging Open Conversations About Mental Health
Destigmatizing mental health discussions is essential for fostering a supportive environment. Encouraging open conversations about mental health allows individuals to share their experiences, seek guidance, and realize they are not alone in their struggles. Creating a culture of understanding reduces the barriers to seeking help.
Promoting Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and stress reduction techniques into daily life can be beneficial for mental wellbeing. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness-based activities help individuals manage stress, improve focus, and cultivate a sense of calm in the midst of uncertainty.
Balancing Work and Personal Life in Remote Environments
The shift to remote work has blurred the boundaries between professional and personal life, contributing to increased stress and burnout. Establishing clear boundaries, taking breaks, and prioritizing work-life balance are crucial for maintaining mental wellbeing in a remote work environment.
Cultivating Hobbies and Creative Outlets
Engaging in hobbies and creative outlets is a constructive way to channel energy and alleviate stress. Whether it’s art, music, writing, or other creative pursuits, dedicating time to activities that bring joy and fulfillment contributes to a more balanced and resilient mental state.
Reflecting on Growth and Resilience
The pandemic has been a collective challenge that has tested the resilience of individuals and communities. Reflecting on personal growth, acknowledging one’s resilience, and recognizing strengths developed during difficult times can foster a positive mindset and outlook for the future.
For more information on nurturing mental wellbeing during the pandemic, visit Mental Wellbeing Pandemic.
Virtual Healing: Telehealth Triumphs in the Pandemic
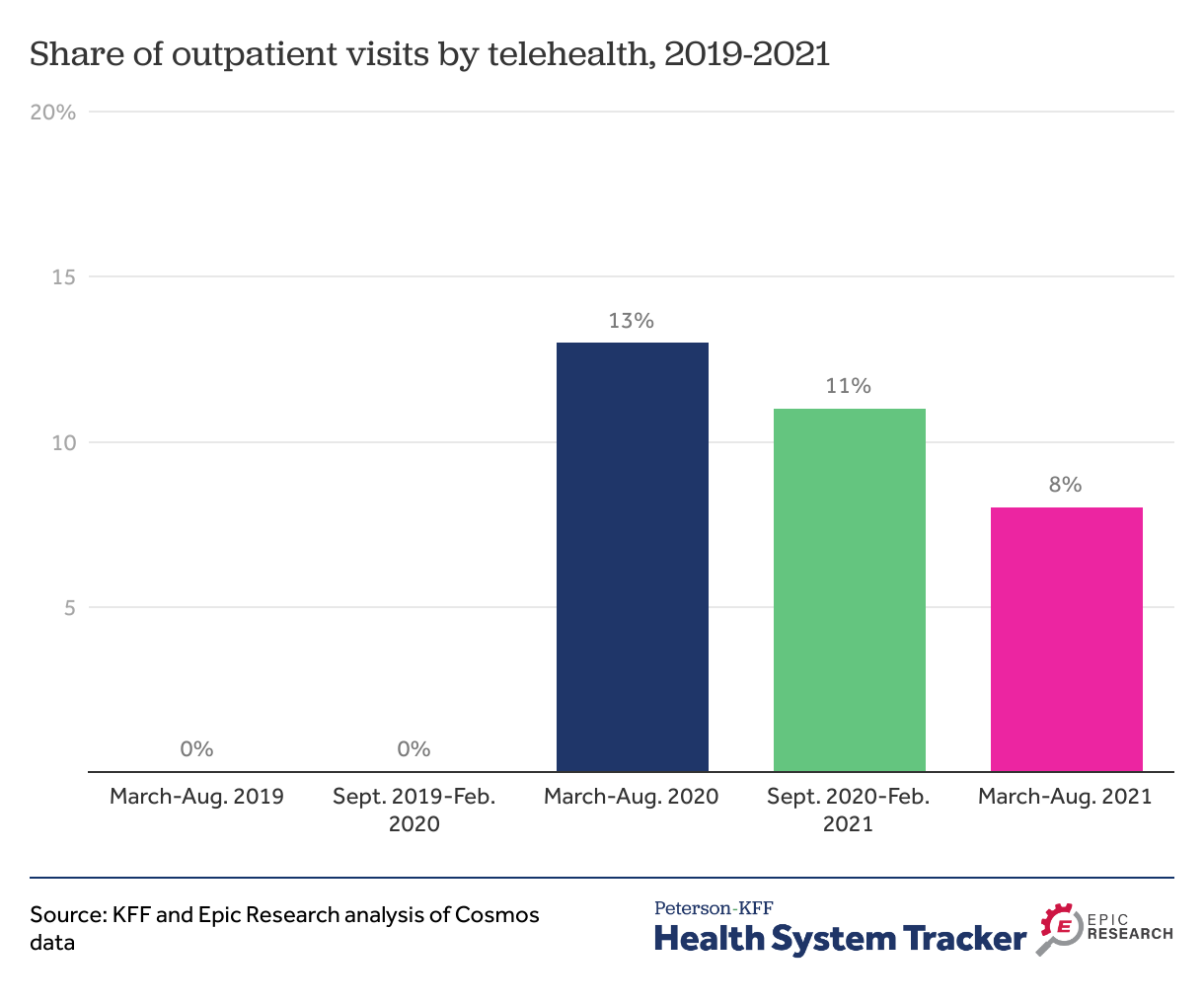
Virtual Healing: Telehealth Triumphs in the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the landscape of healthcare, with telehealth emerging as a transformative solution. This article explores the significant role telehealth has played during the pandemic, its benefits, challenges, and the enduring impact it has on the future of healthcare.
Telehealth During Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on telehealth during the pandemic, visit Telehealth During Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Rise of Telehealth Services:
The pandemic catalyzed the rapid adoption of telehealth services as a means to provide medical care while minimizing physical contact. This section delves into the exponential rise of telehealth platforms, connecting patients with healthcare providers through virtual channels such as video calls, phone consultations, and secure messaging.
Benefits of Telehealth in Pandemic Response:
Telehealth brought forth a myriad of benefits in the pandemic response. This paragraph explores how it enabled timely access to medical advice, reduced the risk of viral transmission in healthcare settings, and provided a lifeline for patients, especially those with chronic conditions, ensuring continuity of care from the safety of their homes.
Expanded Reach and Accessibility:
One notable advantage of telehealth is its ability to overcome geographical barriers. This section discusses how telehealth expanded healthcare accessibility, reaching individuals in remote or underserved areas who might have faced challenges in accessing traditional in-person healthcare services.
Remote Monitoring and Chronic Care Management:
Telehealth proved instrumental in remote monitoring and managing chronic conditions. This paragraph explores how healthcare providers utilized connected devices and wearables to monitor patients’ vital signs, manage chronic diseases, and provide personalized care plans without the need for frequent in-person visits.
Challenges and Solutions in Telehealth Implementation:
Despite its benefits, telehealth faced challenges, including technological barriers, privacy concerns, and the need for regulatory adjustments. This section discusses how healthcare providers and policymakers addressed these challenges through improved technology, enhanced security measures, and streamlined regulations to ensure safe and effective telehealth services.
Telehealth’s Role in Mental Health Support:
The pandemic heightened the need for mental health support, and telehealth emerged as a crucial avenue. This paragraph explores how virtual consultations and therapy sessions provided individuals with access to mental health professionals, reducing stigma, and ensuring ongoing mental health care during challenging times.
Technological Innovations and Integration:
Telehealth spurred technological innovations and integrations in healthcare delivery. This section discusses how artificial intelligence, data analytics, and other technological advancements were integrated into telehealth platforms, enhancing diagnostic capabilities, improving treatment plans, and fostering a more holistic approach to healthcare.
Patient Satisfaction and Quality of Care:
Feedback from patients highlighted high satisfaction levels with telehealth services. This paragraph explores patient experiences, emphasizing the convenience, reduced waiting times, and the positive impact on overall healthcare experiences that telehealth brought to the forefront.
The Future Landscape of Telehealth:
As the pandemic recedes, the impact of telehealth remains significant. This section explores how telehealth has become an integral part of the future healthcare landscape, with hybrid models combining virtual and in-person care likely to persist, offering patients greater flexibility and choice.
Collaboration and Continued Advancements:
The success of telehealth during the pandemic stems from collaborative efforts and ongoing advancements. This paragraph discusses the importance of continued collaboration between healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers to further refine telehealth solutions and ensure its seamless integration into the evolving healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion:
Telehealth has proven to be a transformative force in healthcare, particularly during the challenges posed by the pandemic. From expanding accessibility to providing remote monitoring and mental health support, its benefits are vast. As we look ahead, the lessons learned from the pandemic underscore the enduring role of telehealth in shaping a more resilient, accessible, and patient-centered healthcare system.
Navigating the Mental Health Pandemic: Strategies for Resilience

Navigating the Mental Health Pandemic: Strategies for Resilience
The global landscape has experienced a profound shift, not only in physical health but also in mental well-being. The Mental Health Pandemic has emerged as a critical issue, necessitating comprehensive strategies for resilience and coping.
Understanding the Impact
The ongoing pandemic has brought about unprecedented challenges, affecting people’s mental health on a global scale. From increased stress and anxiety to the exacerbation of pre-existing mental health conditions, the impact is profound and far-reaching.
Breaking the Stigma
One positive aspect of the Mental Health Pandemic is the increased dialogue surrounding mental health issues. Breaking the stigma attached to mental health discussions is crucial for fostering an environment where individuals feel comfortable seeking help and support.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help
Acknowledging the need for professional support is a significant step in navigating the mental health challenges brought on by the pandemic. Mental health professionals play a crucial role in providing guidance, therapy, and coping strategies tailored to individual needs.
Building Resilience Through Mindfulness
Mindfulness practices have gained prominence as effective tools for building resilience. Techniques such as meditation and mindful breathing can help individuals manage stress, stay grounded, and cultivate a positive mindset amidst uncertainty.
Social Connections and Support Networks
Maintaining social connections, even in a physically distanced world, is essential for mental well-being. Utilizing technology for virtual interactions and prioritizing communication with friends and family can provide a valuable support network during challenging times.
Balancing Work and Life
Remote work and lifestyle changes have blurred the lines between professional and personal life, contributing to heightened stress. Establishing clear boundaries, maintaining a routine, and taking breaks are vital for achieving a balance that promotes mental health.
Physical Activity for Mental Well-being
Regular physical activity has proven benefits for both physical and mental health. Engaging in exercise releases endorphins, reduces stress hormones, and provides a natural avenue for improving mood and overall well-being.
Coping with Uncertainty
Uncertainty is a common thread in the fabric of the Mental Health Pandemic. Developing coping mechanisms to deal with uncertainty involves cultivating adaptability, focusing on what can be controlled, and fostering a resilient mindset.
Mental Health Pandemic: A Call to Action
Addressing the Mental Health Pandemic requires collective action. Governments, organizations, and individuals must prioritize mental health resources, support systems, and destigmatize seeking help. Together, we can foster a global environment that values and protects mental well-being.
The Path Forward – Mental Health Pandemic
Visit The Healthy Consumer to explore comprehensive resources and support for navigating the Mental Health Pandemic. Empower yourself with knowledge, connect with professionals, and discover strategies to foster resilience in these challenging times. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and seeking help is a sign of strength.
Health Measures Amid Pandemic: Strategies for Wellness

Navigating Uncertainty: Implementing Pandemic Health Measures for Wellness
The ongoing pandemic has underscored the critical importance of robust health measures in safeguarding individuals and communities. In this article, we explore various strategies for implementing effective pandemic health measures to promote overall wellness.
Understanding the Essentials of Pandemic Health Measures
Comprehensive health measures form the cornerstone of our response to a global pandemic. These measures encompass a range of strategies, from personal hygiene practices to community-wide interventions. Understanding the essentials is crucial for their successful implementation.
Personal Hygiene Practices for Protection
At the individual level, adopting and maintaining rigorous personal hygiene practices is imperative. Regular handwashing, proper use of face masks, and practicing respiratory hygiene contribute significantly to reducing the spread of the virus. These simple yet effective measures play a pivotal role in personal and public health.
Community-Wide Interventions and Social Responsibility
Beyond personal practices, community-wide interventions are essential. Social distancing, crowd limitations, and lockdown measures are tools used to curb the spread of the virus. Embracing these interventions reflects a collective responsibility to protect vulnerable populations and mitigate the impact of the pandemic.
Testing and Contact Tracing: Early Detection Strategies
Early detection is a key element of pandemic health measures. Testing and contact tracing initiatives help identify and isolate cases promptly, preventing further transmission. Implementing widespread testing and efficient contact tracing systems enhances our ability to control outbreaks and protect communities.
Vaccination Campaigns: A Pillar of Prevention
Vaccination campaigns are central to preventing the spread of infectious diseases. In the context of a pandemic, the rapid development and distribution of vaccines are critical. Encouraging vaccination uptake within communities is vital for achieving widespread immunity and overcoming the challenges posed by the virus.
Promoting Mental Health Amidst Health Measures
While physical health measures are paramount, addressing mental health is equally crucial. The stress and uncertainty associated with a pandemic can take a toll on mental well-being. Incorporating mental health support within health measures ensures a holistic approach to wellness during challenging times.
Adapting Health Measures for Varied Settings
Implementing health measures involves adapting strategies to different settings. Whether in workplaces, schools, or public spaces, tailoring interventions to suit the unique dynamics of each setting enhances their effectiveness. Flexibility and responsiveness are key in navigating the complexities of diverse environments.
Communication Strategies: Fostering Understanding and Compliance
Effective communication is fundamental to the success of health measures. Transparent and clear communication fosters understanding and compliance within communities. Keeping the public informed about the rationale behind measures builds trust and encourages active participation in the collective effort to curb the pandemic.
Global Collaboration for Pandemic Health Measures
Addressing a global crisis requires collaboration on an international scale. Sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices enhances the collective response to the pandemic. Collaborative efforts ensure that health measures are informed by a global perspective, fostering resilience and preparedness for future challenges.
Pandemic Health Measures: A Continuous Journey
As we navigate the ongoing challenges posed by the pandemic, implementing and adapting health measures remains a continuous journey. Stay informed about the latest developments in pandemic health measures at Pandemic Health Measures, and let us collectively work towards a healthier and safer future.
Ensuring Workplace Safety: Pandemic Protocols

Navigating Workplace Safety During the Ongoing Pandemic
As workplaces worldwide grapple with the challenges posed by the ongoing pandemic, ensuring the safety of employees has become a top priority. From implementing stringent protocols to embracing technological innovations, organizations are adapting to a new normal in the pursuit of a safe and healthy work environment.
Pandemic Protocols: A Comprehensive Approach
Workplace safety during a pandemic necessitates a comprehensive set of protocols. This includes measures such as social distancing, regular sanitization, and the mandatory use of personal protective equipment (PPE). These protocols, guided by public health recommendations, form the backbone of a resilient strategy to minimize the risk of viral transmission within the workplace.
Remote Work Dynamics and Hybrid Models
The paradigm of work itself has undergone a significant shift during the pandemic. Remote work, once an occasional option, has become a prevalent model. Organizations have embraced remote work dynamics and, in many cases, adopted hybrid models that combine in-office and remote work. This not only enhances workplace safety but also provides employees with flexibility.
Leveraging Technology for Safe Work Environments
Technology emerges as a key ally in the quest for workplace safety. Contactless entry systems, temperature screening devices, and advanced ventilation systems are just a few examples of how technology is being leveraged to create safer work environments. Embracing digital tools for virtual meetings and collaborative work also minimizes physical interactions.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
In the pursuit of workplace safety during a pandemic, employee training and awareness programs play a crucial role. Educating employees about the importance of adherence to safety protocols, proper hand hygiene, and recognizing symptoms fosters a collective responsibility for creating a secure workplace environment.
Mental Health Support in the Workplace
The pandemic has brought to light the importance of mental health in the workplace. Uncertainties, remote work challenges, and the overall stress of the pandemic can impact employees’ mental well-being. Organizations are increasingly focusing on providing mental health support, including counseling services and wellness programs, to ensure a holistic approach to workplace safety.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Work Policies
Flexibility and adaptability in work policies are integral to navigating workplace safety during the pandemic. Organizations are reevaluating sick leave policies, introducing flexible working hours, and creating contingency plans to accommodate various situations. This ensures that employees can prioritize their health without compromising their professional responsibilities.
Collaborative Efforts for Safe Communal Spaces
Communal spaces within workplaces, such as breakrooms and meeting areas, require special attention for maintaining workplace safety. Implementing staggered break times, rearranging seating for social distancing, and encouraging outdoor breaks are among the collaborative efforts organizations are undertaking to create safe communal spaces.
Continuous Monitoring and Response Strategies
Workplace safety is an ongoing commitment that involves continuous monitoring and responsive strategies. Implementing regular health checks, staying informed about the latest developments in public health guidelines, and promptly responding to any potential cases within the workplace contribute to a proactive approach in ensuring safety.
Strategic Communication and Transparency
Communication is key in fostering a culture of workplace safety. Organizations need to maintain transparent communication channels, keeping employees informed about safety measures, updates, and any changes in protocols. This open communication builds trust and reinforces a shared commitment to the well-being of everyone in the workplace.
To explore more insights into workplace safety during the pandemic, visit Workplace Safety Pandemic. As workplaces continue to adapt and evolve, prioritizing the safety and well-being of employees remains paramount. By embracing innovative strategies, technology, and a collective commitment to health, organizations can navigate the challenges of the ongoing pandemic while fostering a safe and resilient work environment.
Navigating Mental Health Challenges During the Pandemic
)
Supporting Mental Health Amidst the Pandemic Challenges
The global pandemic has brought about a surge in mental health challenges, emphasizing the need for robust support systems. Navigating these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of mental well-being.
Understanding the Impact on Mental Health:
The prolonged uncertainty, social isolation, and the fear of the virus have taken a toll on mental health. Understanding the psychological impact of the pandemic is crucial for developing effective strategies to provide support and promote resilience.
Accessible Mental Health Resources:
Amidst the challenges, there is a growing awareness of the importance of accessible mental health resources. Online platforms, teletherapy, and mental health apps have become valuable tools for individuals seeking support. These resources offer a range of services from counseling to mindfulness exercises, catering to diverse needs.
Mental Health Support Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a more detailed guide on mental health support during the pandemic, visit Mental Health Support Pandemic to access valuable resources and insights.
Workplace Mental Health Initiatives:
Recognizing the impact of the pandemic on work-related stress, many companies have implemented workplace mental health initiatives. Employee assistance programs, mental health days, and virtual support groups create a supportive work environment that acknowledges and addresses mental health challenges.
Community Engagement and Connection:
The sense of community and connection plays a pivotal role in mental health support. Social distancing measures have led to increased feelings of isolation. Establishing virtual communities, support networks, and promoting social interactions, even in a digital format, fosters a sense of belonging and support.
Government Policies and Mental Health Advocacy:
Government policies and mental health advocacy have gained prominence as the need for mental health support becomes more apparent. Increased funding for mental health services, destigmatization efforts, and policy changes that prioritize mental well-being contribute to a more supportive environment.
Personal Wellness Practices:
Individuals have embraced personal wellness practices as a means of coping with mental health challenges. Regular exercise, mindfulness, and self-care routines play a crucial role in maintaining mental well-being. Educating individuals about these practices empowers them to take an active role in their mental health.
Crisis Intervention and Helplines:
Crisis intervention services and helplines provide immediate support for individuals in acute distress. These services offer a lifeline for those experiencing overwhelming emotions or crises, ensuring that help is available around the clock.
Education and Mental Health Literacy:
Promoting mental health literacy is essential in normalizing conversations around mental well-being. Educational programs, workshops, and awareness campaigns help debunk myths, reduce stigma, and encourage open dialogue about mental health challenges.
Future Outlook and Continued Support:
As the world navigates the ongoing challenges of the pandemic, the focus on mental health support remains critical. Building a resilient mental health infrastructure involves a continued commitment to accessible resources, community engagement, advocacy, and ongoing education.
Conclusion:
Supporting mental health during the pandemic requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses individual, community, and societal needs. By understanding the impact, promoting accessible resources, fostering workplace initiatives, engaging communities, advocating for policy changes, and prioritizing personal wellness, we can collectively navigate the challenges and build a more supportive and resilient mental health landscape.
Building Community Resilience: Navigating Pandemic Challenges
Introduction
In the face of unprecedented challenges brought on by the global pandemic, the concept of community resilience has become more crucial than ever. Building and strengthening the resilience of communities is not only a collective effort but a necessity for navigating the uncertainties that lie ahead.
Fostering Solidarity and Connection
At the heart of community pandemic resilience is the fostering of solidarity and connection among its members. Communities that come together, support one another, and maintain open lines of communication are better equipped to face the challenges presented by the pandemic. Social cohesion acts as a powerful buffer against the negative impacts of isolation and uncertainty.
Local Leadership and Empowerment
Resilient communities often have strong local leadership that empowers residents to actively participate in decision-making processes. By empowering individuals within the community, local leaders can tap into a diverse range of skills and perspectives, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility that contributes to overall resilience.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
An integral aspect of community resilience is robust emergency preparedness and response mechanisms. Communities that have well-defined plans for emergencies, clear communication channels, and practice regular drills are better prepared to handle unexpected crises, ensuring a swift and coordinated response when needed.
Supporting Vulnerable Populations
In times of crisis, vulnerable populations within a community are often disproportionately affected. Building resilience requires a concerted effort to support and protect these groups. This can involve creating targeted support programs, providing access to essential resources, and ensuring that vulnerable individuals have a voice in community decision-making.
Adapting to Change and Innovation
Resilient communities demonstrate a capacity to adapt to change and embrace innovation. The pandemic has accelerated the need for creative solutions to new challenges. Communities that foster a culture of innovation can find novel ways to address issues, whether it’s supporting local businesses or adapting community services to the evolving needs of residents.
Collaboration with Local Businesses
Local businesses are the backbone of many communities, and their resilience is intertwined with that of the community itself. Collaborative efforts between the community and local businesses, such as supporting buy-local initiatives, can strengthen economic resilience. This symbiotic relationship contributes to the overall well-being of the community.
Crisis Communication and Information Sharing
Effective communication is a cornerstone of community pandemic resilience. Timely and accurate information helps residents make informed decisions, reduces anxiety, and ensures a unified response. Communities that establish reliable communication channels and actively share relevant information contribute to a sense of shared understanding and purpose.
Mental Health and Well-being Support
Prioritizing mental health and well-being is a crucial component of community resilience. Establishing support systems, providing access to mental health resources, and reducing the stigma around seeking help contribute to the overall health of the community. A mentally resilient community can better navigate the challenges posed by the ongoing pandemic.
Sustainable Community Practices
In the pursuit of resilience, communities must also consider sustainability. Practices that promote environmental sustainability, economic stability, and social equity contribute to long-term community well-being. A holistic approach ensures that the community is not only resilient in the face of immediate challenges but also prepared for a sustainable future.
Conclusion with Link
In conclusion, community pandemic resilience is a multifaceted endeavor that requires active participation from all members. Fostering solidarity, supporting vulnerable populations, and embracing innovation are just a few components of building a resilient community. For further insights into community resilience during the pandemic, visit The Healthy Consumer website. Strengthen your community, stay resilient.
Safeguarding Workplaces: Ensuring Safety Amidst Pandemic Challenges

Navigating Workplace Safety During a Pandemic
The unprecedented challenges brought by the pandemic have reshaped the landscape of workplace safety. In this article, we explore key strategies and considerations to ensure the well-being of employees while maintaining operational continuity.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: The Foundation of Workplace Safety
The first step in navigating workplace safety during a pandemic is a thorough risk assessment. Identifying potential hazards and evaluating the risk of exposure within the workplace sets the foundation for effective mitigation strategies. This involves considering factors such as the nature of the work, physical workspace, and the level of interaction among employees.
Implementing Comprehensive Hygiene Protocols: Prioritizing Prevention
A fundamental aspect of workplace safety during a pandemic is the implementation of comprehensive hygiene protocols. This includes promoting frequent handwashing, providing hand sanitizers, and ensuring the cleanliness of shared spaces. Clear communication of these protocols and the importance of personal hygiene contributes to a safer working environment.
Social Distancing Measures: Redefining Workspace Dynamics
Social distancing has become a cornerstone of workplace safety. Redefining workspace dynamics to ensure adequate physical distance between employees helps minimize the risk of viral transmission. This may involve rearranging workstations, limiting the number of employees in common areas, and adopting staggered work schedules.
Remote Work Policies: Balancing Safety and Productivity
In response to the pandemic, many organizations have embraced remote work as a means of ensuring both safety and productivity. Establishing clear remote work policies, providing necessary technology support, and fostering effective communication channels are essential components of a successful remote work strategy.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Enhancing Employee Safety
For industries that require on-site presence, the provision and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are paramount. Masks, gloves, face shields, and other necessary equipment contribute to the enhanced safety of employees. Rigorous training on the correct use and disposal of PPE is crucial to maximize their effectiveness.
Employee Training and Awareness: Empowering the Workforce
Empowering employees with the knowledge and tools to navigate the new workplace safety norms is vital. Conducting regular training sessions on hygiene practices, social distancing, and the proper use of PPE ensures that everyone is well-informed and actively contributes to a safer workplace.
Mental Health Support: Recognizing the Emotional Impact
Workplace safety goes beyond physical health; it includes addressing the emotional impact of the pandemic. Providing mental health support, access to counseling services, and fostering an open dialogue about mental well-being contribute to a supportive and resilient workforce.
Regular Monitoring and Adaptation: Flexibility in Safety Measures
The evolving nature of the pandemic necessitates regular monitoring and adaptation of safety measures. Organizations should stay informed about the latest health guidelines, assess the effectiveness of implemented measures, and adjust protocols accordingly. This flexibility ensures a dynamic response to the changing circumstances.
Communication Channels: Transparency and Open Dialogue
Maintaining transparent communication channels is crucial in fostering a sense of trust and security among employees. Regular updates on safety measures, changes in protocols, and addressing concerns openly contribute to a workplace culture where everyone feels informed and involved in ensuring their safety.
The Role of Workplace Safety Pandemic: A Comprehensive Resource
For additional insights and resources on navigating workplace safety during a pandemic, consider exploring Workplace Safety Pandemic. This centralized hub provides valuable information, best practices, and support for organizations striving to create a safe and secure work environment in the midst of ongoing challenges.
Adapting Education: Remote Learning Strategies Amid Pandemic

Adapting Education: Remote Learning Strategies Amid Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped education, prompting a surge in remote learning. In this article, we explore effective strategies for adapting to the challenges posed by the pandemic and ensuring the success of remote learning initiatives.
Technology Integration: The Backbone of Remote Learning
Integrating technology into education has become paramount in the era of remote learning. Platforms such as video conferencing, online collaboration tools, and learning management systems facilitate seamless communication and interaction between students and educators. Embracing technology is the first step in creating a dynamic and engaging remote learning environment.
Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning: Balancing Flexibility and Interaction
Remote learning allows for a blend of synchronous and asynchronous learning experiences. Synchronous sessions, conducted in real-time, offer opportunities for live interactions, discussions, and immediate feedback. Asynchronous learning, on the other hand, provides flexibility by allowing students to access materials and complete tasks at their own pace. Striking a balance between these approaches accommodates diverse learning preferences.
Engagement Strategies: Fostering Active Participation
Maintaining student engagement is a challenge in remote learning environments. Educators employ various strategies, such as interactive quizzes, polls, and virtual group activities, to foster active participation. Creating a sense of community through online forums and discussion boards also enhances student engagement and contributes to a more enriching learning experience.
Clear Communication: Building Transparent Connections
Clear communication is fundamental in remote learning. Educators must articulate expectations, assignment details, and communication protocols clearly. Regular updates on schedules, assessments, and any changes in the course structure build transparent connections between educators and students. Effective communication minimizes confusion and ensures everyone is on the same page.
Flexible Assessments: Adapting Evaluation Methods
Traditional assessment methods may need modification in a remote learning setting. Implementing a variety of assessment tools, such as online quizzes, written assignments, and project submissions, accommodates different learning styles. Flexibility in assessment methods ensures that students can demonstrate their understanding in ways that suit their strengths.
Professional Development for Educators: Enhancing Digital Literacy
Educators play a crucial role in the success of remote learning. Providing professional development opportunities to enhance digital literacy and teaching skills is essential. Training programs on effective online instruction, technology usage, and adapting curriculum for remote environments empower educators to deliver high-quality education.
Equitable Access to Resources: Addressing Disparities
Ensuring equitable access to resources is a priority in remote learning. Schools must consider the varying levels of access to technology and the internet among students. Implementing solutions, such as providing devices or internet connectivity assistance to those in need, helps address disparities and ensures that all students can fully participate in remote learning.
Supporting Student Well-being: Prioritizing Mental Health
The shift to remote learning can impact student well-being. Educators and institutions must prioritize mental health by creating a supportive environment. This includes fostering open communication, providing resources for stress management, and recognizing the challenges students may face in adapting to remote learning.
Parental Involvement: Collaborating for Success
Remote learning requires collaboration between educators and parents. Keeping parents informed about the curriculum, expectations, and providing guidance on supporting their children’s learning at home fosters a collaborative approach. Regular communication channels, such as virtual parent-teacher meetings, strengthen the partnership between home and school.
Accessing Remote Learning Strategies Pandemic: A Resource Hub
For additional insights and resources on effective remote learning strategies during the pandemic, consider exploring Remote Learning Strategies Pandemic. This centralized hub provides valuable information, best practices, and support for educators, students, and parents navigating the challenges of remote learning in these unprecedented times.




