Critical Hubs: Testing Centers in Pandemic Response

Critical Hubs: Testing Centers in Pandemic Response
As the world grapples with the challenges of the ongoing pandemic, testing centers have emerged as critical hubs in the collective response. This article explores the pivotal role of testing centers in pandemic response, delving into their significance, challenges faced, and the broader impact they have on public health and containment efforts.
Testing Centers Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on testing centers during the pandemic, visit Testing Centers Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Rapid Detection and Early Intervention:
Testing centers serve as frontline facilities for rapid detection of COVID-19 cases, enabling early intervention to mitigate the spread of the virus. Timely testing allows for prompt isolation of individuals who test positive, reducing the risk of transmission within communities and facilitating targeted containment strategies.
Diverse Testing Modalities:
Testing centers offer a range of testing modalities to cater to diverse needs. This includes PCR tests for accurate diagnosis, rapid antigen tests for quick results, and antibody tests to assess previous exposure. The availability of various testing options allows for a flexible and comprehensive approach to pandemic testing.
Community Accessibility and Outreach:
Ensuring community accessibility to testing centers is crucial for widespread testing coverage. Testing facilities are strategically located in communities, offering accessible and convenient locations for individuals to get tested. Outreach efforts, including mobile testing units and pop-up testing sites, further enhance accessibility, reaching underserved populations.
Challenges and Solutions in Testing Logistics:
Despite their critical role, testing centers face logistical challenges such as supply chain disruptions, testing kit shortages, and the need for efficient sample processing. This section explores the challenges encountered by testing centers and the innovative solutions implemented to overcome these hurdles, ensuring uninterrupted testing operations.
Drive-Through and Walk-In Testing Formats:
To enhance accessibility and accommodate different preferences, testing centers often adopt diverse testing formats. Drive-through testing centers allow individuals to get tested without leaving their vehicles, providing a convenient and socially distant option. Simultaneously, walk-in testing sites cater to those who prefer on-site testing without the need for vehicle access.
Integration with Contact Tracing Initiatives:
Testing centers play a vital role in integrating with contact tracing initiatives. By identifying and notifying individuals who may have been exposed to the virus, testing results contribute to a comprehensive approach in controlling the spread. The seamless collaboration between testing centers and contact tracing enhances the effectiveness of containment strategies.
Public Awareness and Education:
Testing centers actively contribute to public awareness and education regarding testing protocols and the importance of getting tested. This involves disseminating clear information about testing eligibility, procedures, and the significance of regular testing, fostering a sense of community responsibility in controlling the pandemic.
Technological Innovations in Testing:
Technological innovations have played a significant role in enhancing testing capabilities. This includes the development of rapid testing technologies, online appointment systems, and digital platforms for result notifications. These innovations streamline the testing process, improve efficiency, and contribute to a more seamless testing experience for individuals.
Global Collaboration and Data Sharing:
Testing centers operate within the broader context of global collaboration and data sharing. This section explores how testing centers contribute to international efforts by sharing data, research findings, and best practices. The collective exchange of information facilitates a more informed and coordinated global response to the pandemic.
Conclusion:
In the intricate tapestry of pandemic response, testing centers emerge as critical hubs, facilitating early detection, community accessibility, and integration with broader containment strategies. Despite facing logistical challenges, these centers continue to adapt, innovate, and contribute significantly to public health efforts. As the world navigates the complexities of the ongoing pandemic, the role of testing centers remains pivotal in safeguarding communities and paving the way towards a more resilient and informed future.
Innovative Solutions: Navigating the Pandemic Response

Innovative Solutions: Navigating the Pandemic Response
The global pandemic has spurred a wave of innovation as communities, businesses, and governments seek effective responses to unprecedented challenges. From healthcare advancements to technological innovations, a multifaceted approach is shaping the way we navigate and overcome the complexities of the pandemic.
Healthcare Innovations and Medical Breakthroughs:
At the forefront of pandemic response innovation are healthcare advancements and medical breakthroughs. The rapid development and distribution of vaccines stand as a testament to the unprecedented collaboration between pharmaceutical companies, researchers, and governments. Beyond vaccines, innovative treatment methods and diagnostic tools have played a pivotal role in managing and mitigating the impact of the virus.
Pandemic Response Innovation: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on pandemic response innovation, visit Pandemic Response Innovation for insights and resources.
Technological Solutions for Remote Work:
The shift towards remote work prompted a surge in technological solutions to facilitate seamless collaboration and productivity. Video conferencing platforms, project management tools, and cybersecurity innovations have become essential components of the remote work landscape. This technological adaptation has not only sustained business operations but has also transformed the way teams collaborate globally.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling:
Data analytics and predictive modeling have played a crucial role in pandemic response strategies. These tools enable health officials to track the spread of the virus, anticipate hotspots, and allocate resources efficiently. The use of data-driven insights has been instrumental in making informed decisions, optimizing healthcare delivery, and enhancing overall response efforts.
Supply Chain Innovations and Resilience:
The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to a renewed focus on supply chain innovations and resilience. Businesses have explored decentralized production, digitalization of logistics, and the use of predictive analytics to ensure a steady flow of essential goods. These innovations aim to build more robust and adaptable supply chains capable of withstanding future disruptions.
Educational Technology and E-Learning Platforms:
With disruptions to traditional education models, there has been a surge in educational technology and e-learning platforms. Virtual classrooms, online resources, and interactive learning tools have become integral to remote education. This shift has not only provided continuity in learning but has also opened up new possibilities for accessible and personalized education.
Telehealth and Virtual Healthcare Services:
Telehealth and virtual healthcare services have experienced unprecedented growth during the pandemic. The ability to consult with healthcare professionals remotely has become a critical component of healthcare delivery. From virtual consultations to remote monitoring, these innovations have enhanced accessibility to medical services and improved overall patient care.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Innovations:
In response to the pandemic, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly innovations. Businesses are adopting environmentally conscious practices, from sustainable packaging to energy-efficient operations. This shift reflects a broader recognition of the interconnectedness between human health, environmental well-being, and overall resilience.
Community-Led Initiatives and Grassroots Innovation:
Communities worldwide have responded to the challenges with grassroots innovation and community-led initiatives. From local makers producing personal protective equipment (PPE) to neighborhood support networks, these initiatives showcase the power of collective action. The sense of community-driven innovation has not only addressed immediate needs but has also fostered a spirit of resilience and solidarity.
Investment in Research and Development:
Governments and private sectors globally have increased their investment in research and development to address current and future health challenges. This commitment to innovation extends beyond the pandemic response to build a foundation for robust healthcare systems, technological advancements, and scientific breakthroughs in the years to come.
Conclusion:
Innovation has been a driving force in navigating the complexities of the pandemic. From healthcare breakthroughs to technological adaptations, supply chain resilience, and community-driven initiatives, the response to the challenges posed by the pandemic has showcased the capacity of human ingenuity. As we continue to face uncertainties, embracing a culture of innovation remains essential in building resilience and shaping a sustainable future.
Navigating Crisis: Effective Pandemic Communication Strategies
Navigating Crisis: Effective Pandemic Communication Strategies
Communication plays a central role in managing crises, and the ongoing pandemic underscores the need for effective strategies to convey information, instill confidence, and foster community resilience. In this article, we delve into essential communication strategies for navigating the challenges posed by the pandemic.
Understanding the Dynamics of Pandemic Communication
Effective pandemic communication begins with an understanding of the unique dynamics of the crisis. This section explores the challenges of conveying information in a rapidly changing environment, addressing misinformation, and catering to diverse audience needs during a global health emergency.
Transparent and Timely Updates for Trust Building
Transparency is the bedrock of effective communication during a pandemic. This part of the article emphasizes the importance of providing transparent and timely updates. Clear information builds trust, alleviates uncertainty, and empowers individuals to make informed decisions for their safety and well-being.
Utilizing Multiple Communication Channels
In the digital age, diverse communication channels are crucial. This section discusses the significance of utilizing multiple platforms, including social media, official websites, press releases, and community forums. A multi-channel approach ensures that information reaches a broad audience and is accessible to different demographic groups.
Tailoring Messages for Diverse Audiences
One size does not fit all in pandemic communication. This part of the article explores the importance of tailoring messages for diverse audiences, considering cultural, linguistic, and demographic factors. Effective communication resonates with the unique needs of various communities and individuals.
Empathy and Emotional Connection
In times of crisis, empathy is a powerful communication tool. This section delves into the importance of expressing empathy in messaging, acknowledging the challenges faced by individuals and communities, and establishing an emotional connection that fosters a sense of unity and support.
Addressing Misinformation and Dispel Myths
Misinformation can spread as rapidly as the virus itself. This part of the article discusses strategies for addressing and correcting misinformation. Effective communication involves actively countering myths, providing factual information, and engaging with the community to dispel inaccuracies.
Engaging with the Community and Seeking Feedback
Two-way communication is essential during a pandemic. This section explores the benefits of actively engaging with the community, seeking feedback, and creating channels for dialogue. Listening to concerns, responding to questions, and adapting communication based on community input enhance overall effectiveness.
Crisis Preparedness Communication Plans
Preparedness is key to effective crisis communication. This part of the article discusses the importance of having robust communication plans in place before a crisis occurs. Organizations and authorities should proactively develop strategies, identify spokespersons, and outline procedures for swift and effective communication.
TheHealthyConsumer.com: A Hub for Pandemic Communication Insights
For comprehensive insights into pandemic communication strategies, visit TheHealthyConsumer.com. The website offers articles, tips, and resources dedicated to understanding and navigating the complexities of communication during these challenging times.
Looking Ahead: Strengthening Communication for Future Crises
In conclusion, effective pandemic communication is a continuous process that evolves with the crisis. This concluding section reflects on the importance of learning from experiences, adapting strategies, and continually strengthening communication for future challenges.
In summary, navigating the complexities of a pandemic requires not just medical expertise but also effective communication strategies. TheHealthyConsumer.com serves as a valuable resource for those seeking guidance on understanding and contributing to the ongoing efforts of pandemic communication in these unprecedented times.
Virtual Healing: Telehealth Triumphs in the Pandemic
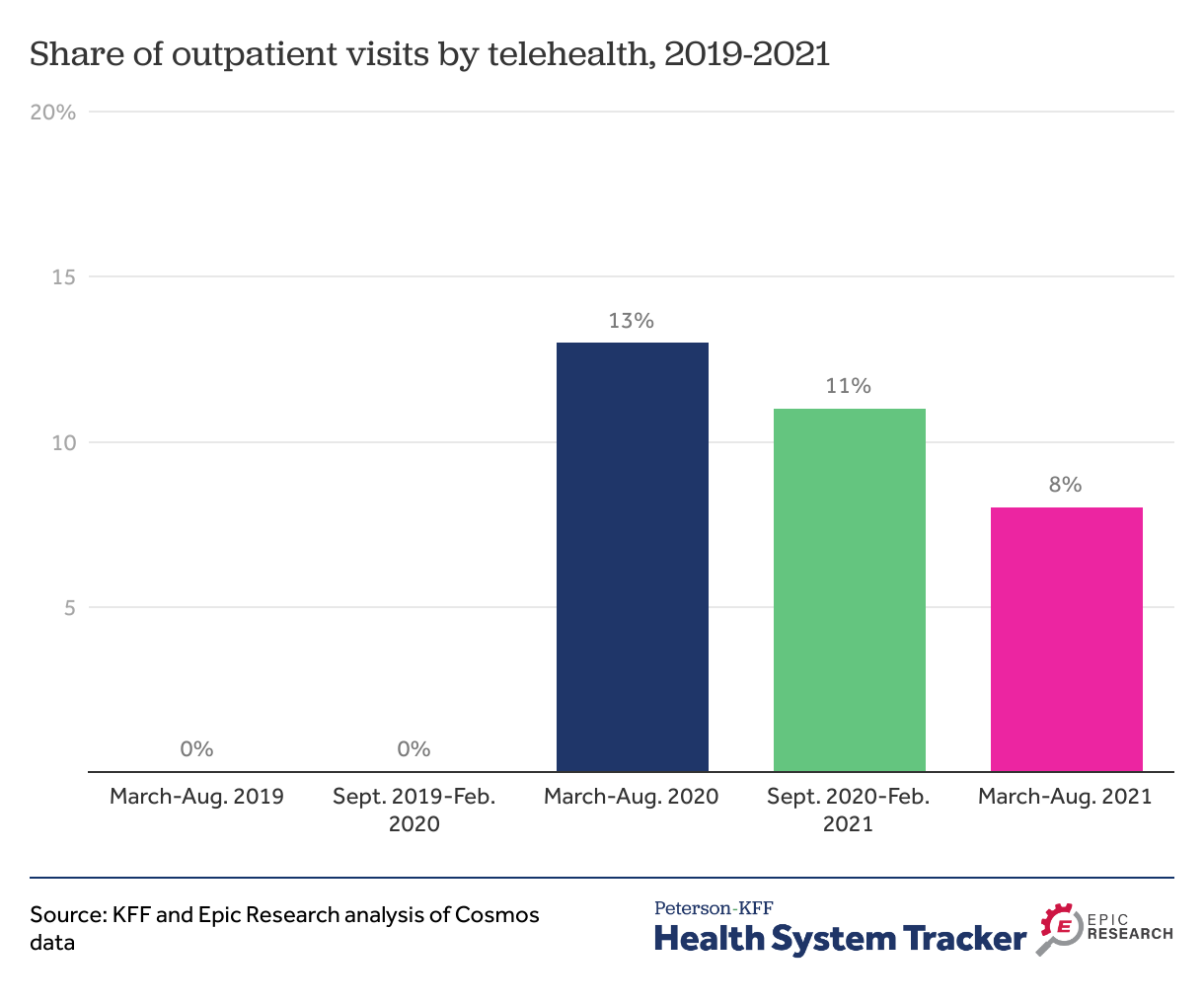
Virtual Healing: Telehealth Triumphs in the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the landscape of healthcare, with telehealth emerging as a transformative solution. This article explores the significant role telehealth has played during the pandemic, its benefits, challenges, and the enduring impact it has on the future of healthcare.
Telehealth During Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on telehealth during the pandemic, visit Telehealth During Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Rise of Telehealth Services:
The pandemic catalyzed the rapid adoption of telehealth services as a means to provide medical care while minimizing physical contact. This section delves into the exponential rise of telehealth platforms, connecting patients with healthcare providers through virtual channels such as video calls, phone consultations, and secure messaging.
Benefits of Telehealth in Pandemic Response:
Telehealth brought forth a myriad of benefits in the pandemic response. This paragraph explores how it enabled timely access to medical advice, reduced the risk of viral transmission in healthcare settings, and provided a lifeline for patients, especially those with chronic conditions, ensuring continuity of care from the safety of their homes.
Expanded Reach and Accessibility:
One notable advantage of telehealth is its ability to overcome geographical barriers. This section discusses how telehealth expanded healthcare accessibility, reaching individuals in remote or underserved areas who might have faced challenges in accessing traditional in-person healthcare services.
Remote Monitoring and Chronic Care Management:
Telehealth proved instrumental in remote monitoring and managing chronic conditions. This paragraph explores how healthcare providers utilized connected devices and wearables to monitor patients’ vital signs, manage chronic diseases, and provide personalized care plans without the need for frequent in-person visits.
Challenges and Solutions in Telehealth Implementation:
Despite its benefits, telehealth faced challenges, including technological barriers, privacy concerns, and the need for regulatory adjustments. This section discusses how healthcare providers and policymakers addressed these challenges through improved technology, enhanced security measures, and streamlined regulations to ensure safe and effective telehealth services.
Telehealth’s Role in Mental Health Support:
The pandemic heightened the need for mental health support, and telehealth emerged as a crucial avenue. This paragraph explores how virtual consultations and therapy sessions provided individuals with access to mental health professionals, reducing stigma, and ensuring ongoing mental health care during challenging times.
Technological Innovations and Integration:
Telehealth spurred technological innovations and integrations in healthcare delivery. This section discusses how artificial intelligence, data analytics, and other technological advancements were integrated into telehealth platforms, enhancing diagnostic capabilities, improving treatment plans, and fostering a more holistic approach to healthcare.
Patient Satisfaction and Quality of Care:
Feedback from patients highlighted high satisfaction levels with telehealth services. This paragraph explores patient experiences, emphasizing the convenience, reduced waiting times, and the positive impact on overall healthcare experiences that telehealth brought to the forefront.
The Future Landscape of Telehealth:
As the pandemic recedes, the impact of telehealth remains significant. This section explores how telehealth has become an integral part of the future healthcare landscape, with hybrid models combining virtual and in-person care likely to persist, offering patients greater flexibility and choice.
Collaboration and Continued Advancements:
The success of telehealth during the pandemic stems from collaborative efforts and ongoing advancements. This paragraph discusses the importance of continued collaboration between healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers to further refine telehealth solutions and ensure its seamless integration into the evolving healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion:
Telehealth has proven to be a transformative force in healthcare, particularly during the challenges posed by the pandemic. From expanding accessibility to providing remote monitoring and mental health support, its benefits are vast. As we look ahead, the lessons learned from the pandemic underscore the enduring role of telehealth in shaping a more resilient, accessible, and patient-centered healthcare system.
Strategic Containment: Navigating the Pandemic Challenges

Strategic Containment: Navigating the Pandemic Challenges
The global pandemic has necessitated the development and implementation of strategic containment strategies to curb the spread of the virus and mitigate its impact on public health and society. This article explores the multifaceted nature of containment strategies, shedding light on their importance and diverse applications in navigating the challenges posed by the ongoing pandemic.
Containment Strategies Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on containment strategies during the pandemic, visit Containment Strategies Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Testing and Early Detection:
One of the key pillars of strategic containment is widespread testing and early detection of COVID-19 cases. Timely identification allows for prompt isolation and treatment, preventing further transmission. Robust testing infrastructure and widespread availability of testing facilities contribute to effective containment efforts.
Quarantine and Isolation Protocols:
Implementing effective quarantine and isolation protocols is essential to prevent the spread of the virus. Individuals who have been exposed to the virus or tested positive must adhere to isolation guidelines. Clear communication of these protocols and support for those in isolation are crucial components in ensuring compliance.
Contact Tracing Initiatives:
Contact tracing plays a vital role in identifying and notifying individuals who may have been exposed to the virus. Technology, such as mobile apps and digital tools, has been employed to enhance the efficiency of contact tracing efforts. Balancing privacy concerns while maximizing the effectiveness of contact tracing remains a key consideration.
Vaccination Rollout Programs:
The rollout of vaccination programs is a cornerstone in the strategic containment of the pandemic. Governments and health authorities globally have worked to ensure the equitable distribution of vaccines, aiming to achieve widespread immunity. Vaccination not only protects individuals from severe illness but also contributes to community-wide immunity.
Public Health Awareness Campaigns:
Public health awareness campaigns are instrumental in fostering a sense of shared responsibility and educating the public about containment measures. These campaigns disseminate accurate information about the virus, vaccination, and preventive measures. Clear and consistent messaging helps build trust and encourages adherence to recommended guidelines.
Travel Restrictions and Border Control:
Strategic containment extends to travel restrictions and border control measures. Governments have implemented various restrictions on international and domestic travel to limit the movement of the virus. Monitoring and regulating border crossings contribute to preventing the introduction and spread of new variants.
Hygiene Practices and Protective Measures:
Promoting hygiene practices and protective measures is essential in containing the virus’s spread. Emphasizing the importance of regular handwashing, mask-wearing, and maintaining physical distancing contributes to minimizing the risk of transmission in various settings, including public spaces and workplaces.
Community Engagement and Empowerment:
Engaging communities and empowering individuals to actively participate in containment efforts is crucial. Communities play a central role in adherence to guidelines, supporting those affected, and fostering a collective commitment to containment. Empowering individuals through education and community involvement strengthens the overall effectiveness of containment strategies.
Adaptability and Data-Driven Decision-Making:
The dynamic nature of the pandemic requires an adaptable approach to containment strategies. Utilizing real-time data and analytics enables authorities to make informed decisions based on the evolving situation. Flexibility in adjusting strategies based on data trends contributes to the effectiveness of containment efforts.
Global Collaboration for Comprehensive Containment:
Strategic containment is not limited by national borders, emphasizing the need for global collaboration. Sharing information, resources, and best practices on a global scale contributes to comprehensive containment. International cooperation in vaccine distribution, research, and containment strategies fosters a united front against the pandemic.
Conclusion:
Strategic containment strategies are pivotal in navigating the challenges posed by the ongoing pandemic. From widespread testing and early detection to quarantine protocols, contact tracing initiatives, vaccination rollout programs, public health awareness campaigns, travel restrictions, hygiene practices, community engagement, adaptability, and global collaboration, each aspect contributes to a comprehensive and effective containment approach. As the world continues to combat the virus, a strategic and collaborative containment strategy remains essential in safeguarding public health and promoting a swift recovery.
Navigating Crisis: Pandemic Management Strategies
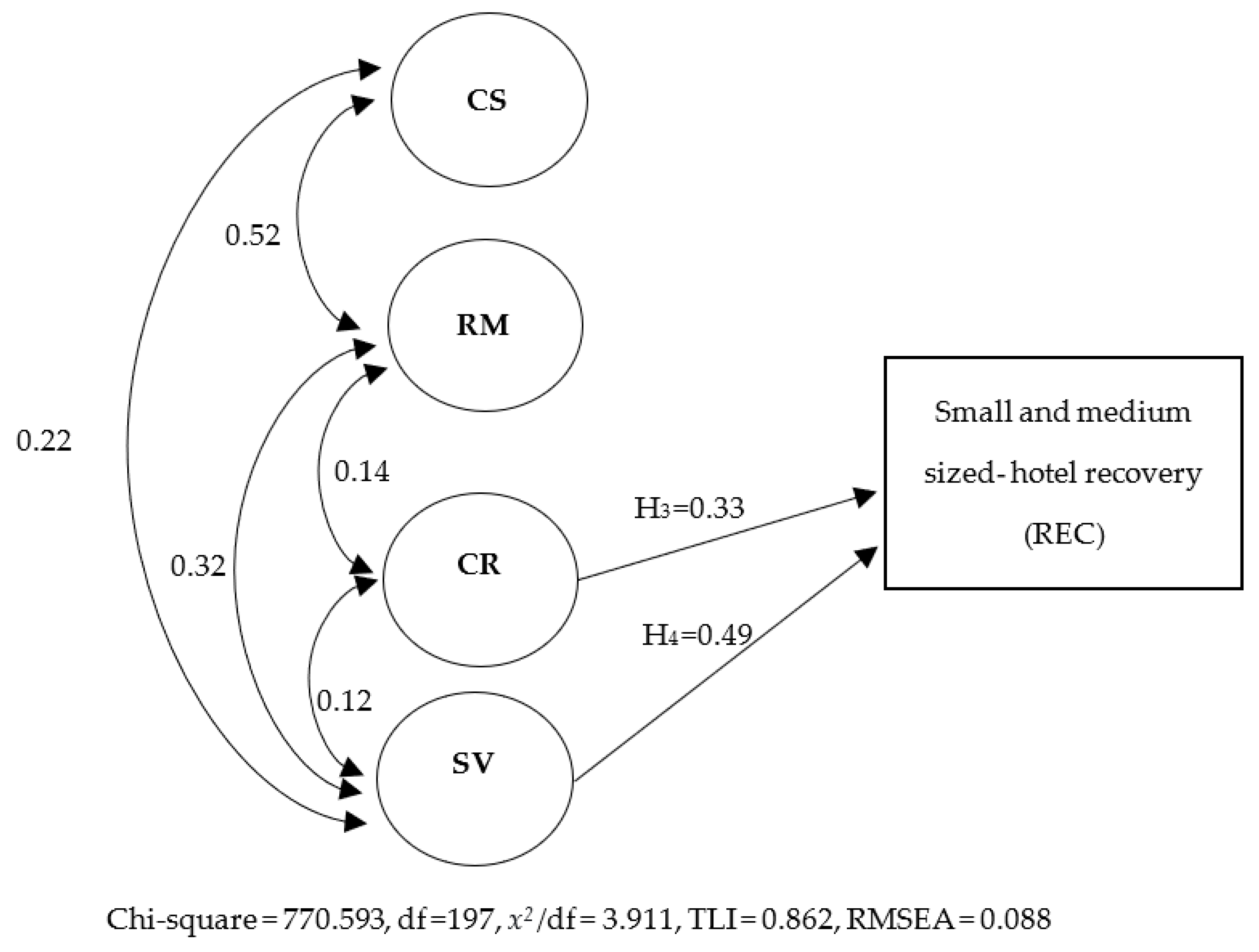
Strategies for Navigating Crisis: Pandemic Management Unveiled
The global pandemic has tested the resilience of individuals, communities, and organizations. In this article, we delve into effective crisis management strategies amidst the ongoing pandemic, exploring key principles to guide us through these challenging times.
Understanding the Nature of the Crisis: A Foundation for Action
Effective crisis management begins with a clear understanding of the nature of the crisis. In the case of a pandemic, comprehending the virus’s characteristics, transmission methods, and potential impacts is crucial. This knowledge forms the foundation for informed decision-making and proactive responses.
Establishing a Crisis Management Team: Coordinated Leadership
Central to navigating a crisis is the formation of a dedicated crisis management team. This team, comprised of individuals with diverse expertise, ensures a comprehensive approach to addressing challenges. Coordinated leadership, quick decision-making, and clear communication are hallmarks of an effective crisis management team.
Communication is Key: Transparent and Timely Information
Transparent and timely communication is paramount during a crisis. Keeping stakeholders informed fosters trust and helps manage anxiety. Regular updates on the situation, preventive measures, and response efforts are essential. Utilizing various communication channels ensures information reaches a broad audience.
Implementing Preventive Measures: Proactive Risk Mitigation
Proactive measures play a vital role in crisis management. Implementing preventive measures, such as social distancing, hygiene protocols, and travel restrictions during a pandemic, helps mitigate the risk of spreading the virus. A comprehensive strategy that prioritizes public health is fundamental to crisis containment.
Adapting Business Continuity Plans: Ensuring Operational Resilience
Organizations must adapt their business continuity plans to navigate the challenges posed by a pandemic. This involves identifying critical functions, establishing remote work capabilities, and securing supply chains. Flexibility and adaptability are key elements in ensuring operational resilience during times of crisis.
Crisis Response and Resource Allocation: Agility in Action
The ability to respond swiftly and allocate resources effectively is a defining aspect of crisis management. This agility requires a dynamic response plan that can be adjusted based on evolving circumstances. Allocating resources strategically ensures that essential needs are met and crisis impacts are minimized.
Fostering a Resilient Organizational Culture: Employee Support
Maintaining a resilient organizational culture is essential during a crisis. Prioritizing employee well-being, offering support services, and fostering a sense of community contribute to a resilient workforce. Investing in employee mental health programs helps mitigate the emotional toll of the crisis.
Learning from the Crisis: Post-Crisis Analysis and Adaptation
Post-crisis analysis is a critical component of effective crisis management. Conducting a thorough review of actions taken, identifying areas for improvement, and incorporating lessons learned into future crisis plans enhances an organization’s overall resilience. Continuous adaptation is key in an ever-changing landscape.
Global Collaboration for Pandemic Management: Uniting Against a Common Foe
The interconnected nature of a pandemic necessitates global collaboration. Sharing information, resources, and best practices on an international scale enhances collective efforts. Collaborative initiatives, such as vaccine distribution programs and research partnerships, showcase the power of united action against a common foe.
In the midst of navigating these crisis management strategies, individuals and organizations can find additional insights and support through resources such as Crisis Management Pandemic. This centralized hub offers guidance on crisis response, risk mitigation, and fostering resilience in the face of ongoing challenges.
Advancing Vaccination: Global Efforts Amid Pandemic Challenges
Navigating the Global Challenge: Advancing Vaccination Efforts Amid the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred an unprecedented global effort to develop and distribute vaccines. As countries grapple with the challenges of mass vaccination campaigns, the collective endeavor to inoculate populations and achieve herd immunity is a testament to the power of science, collaboration, and resilience.
Research and Development Breakthroughs
The journey to combatting the pandemic began with groundbreaking research and development efforts. Scientists and pharmaceutical companies worldwide worked tirelessly to create effective vaccines against the novel coronavirus. The rapid development and approval of multiple vaccines marked a historic achievement in the field of medicine.
Challenges in Distribution and Accessibility
While vaccines offer hope, their distribution poses a significant challenge. Ensuring equitable access to vaccines across the globe has been a complex undertaking. Issues such as supply chain disruptions, vaccine hesitancy, and logistical hurdles have highlighted the need for coordinated international efforts to address disparities and promote inclusivity.
Vaccine Diplomacy and International Collaboration
Vaccination efforts have transcended national borders, with countries engaging in vaccine diplomacy and collaborative initiatives. The sharing of vaccine doses, technology transfer, and financial support for global vaccination programs underscore the importance of solidarity in overcoming a shared global threat.
Public Health Communication and Education
Addressing vaccine hesitancy and promoting public awareness have been integral to successful vaccination campaigns. Clear and transparent communication about vaccine safety, efficacy, and the importance of community immunity is crucial in fostering public trust and encouraging widespread vaccine acceptance.
Role of Technology in Vaccination Campaigns
Technology has played a pivotal role in streamlining vaccination campaigns. From online appointment systems to vaccine tracking apps, digital solutions have enhanced the efficiency of vaccine distribution. Embracing technology has allowed for real-time data analysis and better coordination among healthcare providers.
Community Engagement and Grassroots Initiatives
Community engagement is key to the success of vaccination efforts. Grassroots initiatives, involving local leaders, community organizations, and volunteers, contribute to reaching underserved populations. Tailoring vaccination strategies to the specific needs and concerns of communities ensures a more inclusive and effective campaign.
Overcoming Variants and Ongoing Challenges
The emergence of new virus variants presents an ongoing challenge to vaccination efforts. Continuous research, vaccine adaptations, and international cooperation are essential in addressing evolving threats. Flexibility and preparedness remain critical in the face of uncertainties surrounding the long-term effectiveness of existing vaccines.
Impact on Global Travel and Economic Recovery
The success of vaccination efforts has direct implications for global travel and economic recovery. Many countries tie the reopening of borders and resumption of normal economic activities to vaccination rates. Achieving widespread immunity is a crucial milestone in revitalizing industries and restoring international mobility.
The Way Forward: Building a Resilient Future
As vaccination efforts progress, the world stands at a critical juncture in the fight against the pandemic. The lessons learned from the challenges faced in distributing and administering vaccines provide valuable insights for future global health initiatives. Building a more resilient healthcare infrastructure and fostering international collaboration are key to preventing and mitigating future pandemics.
For more information on the ongoing vaccination efforts amid the pandemic, visit Vaccination Efforts Pandemic.
Strategic Responses: Navigating Pandemic Challenges

Crafting Effective Responses: Navigating Pandemic Challenges
The unprecedented challenges posed by a global pandemic demand strategic and adaptive responses. In navigating these complex scenarios, effective pandemic response strategies emerge as crucial tools for mitigating the impact, safeguarding communities, and fostering resilience.
Understanding the Dynamic Nature of Pandemics
The foundation of effective pandemic response lies in a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic nature of these global health crises. Recognizing that pandemics evolve, presenting different challenges at various stages, allows for the formulation of strategies that are agile, adaptive, and rooted in real-time data and insights.
Collaborative Governance and Interagency Coordination
A successful pandemic response requires collaborative governance and seamless interagency coordination. Governments, healthcare systems, and relevant agencies must work together cohesively. Establishing clear communication channels, sharing resources, and coordinating efforts ensure a unified response that is vital in managing the complexities of a pandemic.
Implementing Early Detection and Surveillance Systems
Early detection is paramount in controlling the spread of a pandemic. Implementing robust surveillance systems, both at local and global levels, facilitates early identification of outbreaks. Monitoring trends, analyzing data, and swiftly responding to emerging threats enable authorities to contain and manage the impact of the pandemic effectively.
Strategic Testing and Contact Tracing Initiatives
Strategic testing and contact tracing initiatives form the bedrock of a targeted response. Widespread and accessible testing, coupled with efficient contact tracing, allows for the identification and isolation of cases promptly. This strategic approach helps break the chains of transmission and prevents the exponential spread of the virus.
Healthcare System Preparedness and Capacity Building
Ensuring the preparedness and capacity of healthcare systems is a critical aspect of pandemic response. This involves strengthening healthcare infrastructure, securing adequate medical supplies, and enhancing the capacity of healthcare professionals. A robust healthcare system is essential for managing the influx of patients and providing quality care.
Communication and Public Awareness Campaigns
Transparent and timely communication is indispensable in a pandemic response. Implementing effective communication strategies and public awareness campaigns disseminate accurate information, dispel myths, and foster a sense of collective responsibility. Informed communities are more likely to adhere to preventive measures, contributing to the overall success of the response.
Balancing Social and Economic Impacts
Pandemic response strategies must strike a delicate balance between addressing the health crisis and mitigating social and economic impacts. Implementing measures to support individuals and businesses affected by the pandemic, such as financial aid packages, unemployment support, and targeted economic stimulus, contributes to a more holistic response.
Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations and Equity
An equitable pandemic response prioritizes the needs of vulnerable populations. This includes the elderly, individuals with underlying health conditions, and marginalized communities. Tailoring strategies to address the specific challenges faced by these groups ensures that the response is inclusive and leaves no one behind.
International Cooperation and Information Sharing
Pandemics transcend borders, underscoring the importance of international cooperation. Sharing information, expertise, and resources on a global scale enhances the collective response. Collaborative efforts among nations foster a sense of solidarity and enable a more effective and coordinated approach to managing and overcoming the pandemic.
To delve deeper into effective pandemic response strategies, visit Pandemic Response Strategies. As the world grapples with the challenges posed by global health crises, implementing thoughtful and strategic responses is imperative. By understanding the evolving nature of pandemics, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing the well-being of communities, nations can navigate these challenges with resilience and effectiveness.
Navigating Pandemic Challenges: Essential Response Tips

Strategies for Navigating Pandemic Challenges: Essential Response Tips
The ongoing pandemic has thrust individuals and communities into unprecedented circumstances, demanding thoughtful and effective responses. In this article, we explore key tips for navigating the challenges presented by the pandemic and maintaining resilience.
Staying Informed: The Cornerstone of Effective Response
In the face of rapidly evolving circumstances, staying informed is crucial. Regularly check reliable sources for updates on the pandemic’s status, health guidelines, and government recommendations. An informed approach forms the basis for making sound decisions and taking proactive measures to protect oneself and others.
Prioritizing Personal Health: A Foundation for Resilience
One of the most fundamental response tips is to prioritize personal health. This includes adhering to recommended hygiene practices, maintaining a nutritious diet, staying physically active, and getting sufficient sleep. Strengthening individual health is a proactive measure that contributes to overall resilience in the face of the pandemic.
Adapting to Remote Work: Navigating the New Normal
For those whose work allows it, adapting to remote work has become a significant aspect of pandemic response. Establishing a dedicated workspace, maintaining a routine, and utilizing collaboration tools effectively are key elements for a successful transition to remote work. Balancing professional and personal life becomes essential in this new normal.
Embracing Technology for Connection: Overcoming Social Distancing
While physical distancing is crucial for public health, maintaining social connections is equally important. Embrace technology to stay connected with friends, family, and colleagues. Virtual gatherings, video calls, and online activities can help alleviate feelings of isolation and foster a sense of community during these challenging times.
Financial Planning and Budgeting: Building Financial Resilience
The economic impact of the pandemic underscores the importance of financial planning. Assess your financial situation, create a budget, and prioritize essential expenses. Building financial resilience involves exploring opportunities for saving, identifying potential sources of support, and adapting spending habits to navigate economic uncertainties.
Caring for Mental Well-being: Seeking Support and Coping Strategies
The pandemic has brought about heightened stress and anxiety. Prioritize mental well-being by seeking support when needed. This may involve talking to friends, family, or mental health professionals. Additionally, incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as mindfulness, exercise, or hobbies.
Community Engagement: Supporting and Being Supported
Communities play a crucial role in pandemic response. Look for opportunities to support local businesses, volunteer, or contribute to community initiatives. Engaging with your community fosters a sense of solidarity and provides mutual support during challenging times.
Flexible Planning for the Future: Anticipating and Adapting
Pandemic response involves flexible planning for an uncertain future. Anticipate potential challenges, but remain adaptable. Set realistic goals, reassess plans regularly, and be open to adjusting strategies based on evolving circumstances. Flexibility is a key attribute in navigating the dynamic nature of the pandemic.
Educational and Skill Development: Investing in Personal Growth
Use the time during the pandemic as an opportunity for personal growth and skill development. Online courses, virtual workshops, and self-directed learning can enhance your knowledge and skills. Investing in education not only contributes to personal development but also positions you for future opportunities.
Accessing Pandemic Response Tips: A Comprehensive Resource
For additional insights and resources on navigating the challenges of the pandemic, consider exploring Pandemic Response Tips. This centralized hub offers a wealth of information, practical tips, and support to help individuals and communities navigate the complexities of the ongoing pandemic with resilience and determination.





