Global Vigilance: Preventing International Pandemics

Elevating Global Vigilance: International Pandemic Prevention
The interconnected nature of our world has magnified the importance of international collaboration in preventing and mitigating pandemics. As the global community continues to grapple with the aftermath of recent health crises, the imperative of international pandemic prevention becomes increasingly evident.
The Urgent Need for Cross-Border Cooperation
International pandemic prevention demands a unified effort that transcends borders. The movement of people, goods, and information across the globe necessitates collaborative strategies among nations. Shared knowledge, resources, and coordinated response mechanisms are crucial components in mitigating the risk and impact of potential pandemics.
Global Surveillance and Early Warning Systems
Surveillance and early warning systems on a global scale are pivotal in detecting and responding to potential pandemics swiftly. International organizations, in collaboration with member countries, play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining these systems. Timely identification of emerging threats allows for a proactive and targeted response.
Cross-Sectoral Collaboration for Resilience
Pandemic prevention involves collaboration not only among nations but also across various sectors. Governments, healthcare organizations, research institutions, and private industries must work together seamlessly. This cross-sectoral collaboration ensures a comprehensive and multifaceted approach, addressing both the medical and socio-economic aspects of pandemic prevention.
Global Health Diplomacy as a Cornerstone
Global health diplomacy emerges as a cornerstone in fostering international cooperation for pandemic prevention. Diplomatic efforts are crucial in facilitating the exchange of information, expertise, and resources. Building diplomatic relationships and trust among nations establishes a foundation for effective collaboration during times of crisis.
Investment in Healthcare Infrastructure Worldwide
Ensuring global pandemic prevention requires an investment in healthcare infrastructure worldwide. Developing nations, in particular, need support to strengthen their healthcare systems. Adequate healthcare infrastructure is a bulwark against the rapid spread of infectious diseases and facilitates a more coordinated response to emerging health threats.
Research and Innovation for Anticipating Challenges
International collaboration in research and innovation is paramount for anticipating and addressing future challenges. Shared research efforts contribute to the development of vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools. Collaborative initiatives enhance the global community’s preparedness to combat novel pathogens and evolving health risks.
Capacity Building for Rapid Response
Building the capacity for rapid response is a key aspect of international pandemic prevention. This involves training healthcare professionals, establishing emergency response teams, and pre-positioning medical supplies. A well-prepared and trained workforce ensures a swift and effective response to contain and manage the spread of infectious diseases.
Public Health Education on a Global Scale
International pandemic prevention also hinges on public health education on a global scale. Promoting awareness, disseminating accurate information, and encouraging preventive practices empower individuals to play an active role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Informed and engaged communities are essential components of a resilient global health defense.
Multilateral Agreements for Coordinated Action
Multilateral agreements that outline coordinated actions in times of pandemics are critical for international collaboration. These agreements establish a framework for joint responses, resource-sharing, and support mechanisms. Clear protocols for communication and assistance enhance the effectiveness of collaborative efforts in preventing and managing pandemics.
To explore comprehensive insights into international pandemic prevention, visit International Pandemic Prevention. As the world navigates the complexities of global health challenges, a united and proactive international approach is crucial. By fostering collaboration, investing in global health infrastructure, and prioritizing research and education, nations can collectively build a resilient defense against the threats of pandemics.
Containment Mastery: Strategies for Pandemic Triumph
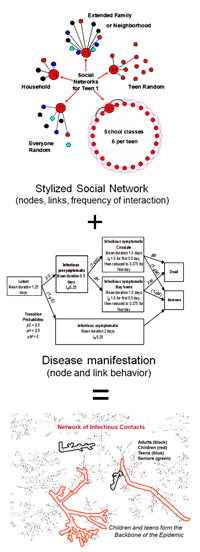
Introduction
In the battle against a pandemic, effective containment strategies are the linchpin for triumph. This article delves into the essential strategies employed to contain a pandemic, exploring the multifaceted approaches that contribute to curbing the spread of infectious diseases and safeguarding global health.
Early Detection and Surveillance
The foundation of pandemic containment lies in early detection and surveillance. Timely identification of potential outbreaks allows for swift response measures. Robust surveillance systems, monitoring symptoms and testing, enable health authorities to track and trace the virus, preventing its uncontrolled spread within communities.
Strategic Quarantine and Isolation Measures
Strategic quarantine and isolation measures play a pivotal role in limiting the transmission of infectious diseases. By isolating confirmed cases and implementing targeted quarantines for individuals at risk, authorities can break the chains of transmission and prevent widespread community outbreaks.
Mass Testing Initiatives
Mass testing initiatives are a key component of containment strategies. Implementing widespread testing allows for the identification of asymptomatic carriers and early intervention. By expanding testing capabilities and accessibility, health authorities can quickly identify and isolate individuals who may unknowingly spread the virus.
Effective Contact Tracing
Contact tracing is a meticulous process that involves identifying and notifying individuals who have been in close contact with confirmed cases. Leveraging technology, efficient contact tracing systems streamline the identification process, enabling rapid notification, testing, and isolation of potentially exposed individuals.
Stringent Travel Restrictions
In a globally connected world, travel can contribute significantly to the spread of infectious diseases. Implementing stringent travel restrictions, including border controls, quarantine protocols, and travel bans when necessary, is a crucial strategy to prevent the introduction and exportation of the virus across regions.
Public Health Education and Communication
Effective containment strategies rely on clear and consistent public health education and communication. Informing the public about the virus, preventive measures, and the importance of adherence to guidelines fosters a collective understanding. Transparent communication builds trust and encourages widespread compliance.
Vaccination Campaigns
Vaccination is a cornerstone in the long-term containment of a pandemic. Rapid and widespread vaccination campaigns contribute to achieving herd immunity, reducing the severity of illness, and preventing the uncontrolled spread of the virus. Vaccination efforts are integral to ending the pandemic and preventing future outbreaks.
Community Engagement and Cooperation
Containment strategies are most effective when communities actively engage and cooperate. Fostering community cooperation through outreach, education, and collaboration with local leaders builds a unified front against the virus. Communities that actively participate in containment efforts contribute significantly to overall success.
Adaptive Governance and Response
Adaptive governance and response are critical in the face of a rapidly evolving pandemic. Governments and health authorities must continuously assess the situation, adapt strategies based on emerging data, and deploy resources where they are most needed. An agile and responsive approach enhances the effectiveness of containment measures.
International Collaboration for Global Health
Pandemics transcend borders, necessitating international collaboration for global health security. Sharing information, resources, and expertise across nations strengthens the collective response to the pandemic. International cooperation is vital for developing and implementing containment strategies that address the interconnected nature of global health.
Conclusion with Link
In conclusion, pandemic containment strategies require a multifaceted and collaborative approach. For further insights into effective containment strategies and global health security, visit The Healthy Consumer website. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and contribute to the triumph over pandemics.
Strategic Pandemic Containment: Effective Global Approaches

Strategic Pandemic Containment: Effective Global Approaches
In the ongoing battle against global health crises, understanding and implementing effective Pandemic Containment Strategies are paramount. This article delves into the multifaceted approaches that contribute to successfully containing pandemics on a global scale.
Early Detection and Surveillance
Pandemic Containment begins with early detection and robust surveillance systems. Identifying and monitoring potential outbreaks allow for swift responses, enabling authorities to implement containment measures before the situation escalates. Surveillance is a cornerstone in preventing the rapid spread of infectious diseases.
Strategic Testing and Contact Tracing
Strategic testing and contact tracing are integral components of Pandemic Containment Strategies. Widely available testing, combined with efficient contact tracing, helps identify and isolate infected individuals promptly. This proactive approach disrupts the chain of transmission and limits the spread of the virus.
Quarantine and Isolation Protocols
Implementing effective quarantine and isolation protocols is crucial in controlling the spread of a pandemic. By isolating infected individuals and quarantining those exposed, authorities can minimize the risk of widespread transmission. Clear guidelines and communication are essential for public adherence to these protocols.
Vaccination Campaigns and Immunization
A cornerstone in Pandemic Containment is widespread vaccination. Vaccination campaigns contribute to achieving population immunity, reducing the severity of illness, and preventing further spread. Ensuring equitable access to vaccines globally is essential for comprehensive and effective containment.
Public Health Education and Communication
Transparent and accessible communication is vital in Pandemic Containment. Public health education campaigns inform the public about the virus, preventive measures, and the importance of cooperation. Clear and consistent messaging fosters a sense of shared responsibility and encourages adherence to guidelines.
Global Cooperation and Data Sharing
Global cooperation is indispensable in Pandemic Containment. Countries and organizations must share information, resources, and expertise. Collaborative efforts enhance the collective response, allowing for a more unified approach to challenges such as vaccine distribution, research, and containment strategies.
Adaptive Policy Implementation
Flexibility in policy implementation is key in dynamic situations. Governments and health authorities must adapt Pandemic Containment Strategies based on evolving circumstances. This adaptability ensures that responses remain effective in addressing the unique challenges posed by each phase of a pandemic.
Community Engagement and Support
Pandemic Containment is more effective when communities actively participate. Engaging the public through community outreach programs, addressing concerns, and providing support fosters a sense of shared responsibility. Communities become active partners in the fight against the pandemic.
Technological Innovations in Containment
Technological innovations play a pivotal role in Pandemic Containment. From contact tracing apps to data analytics, technology enhances the efficiency of containment efforts. Embracing and continually improving these innovations contribute to more effective and data-driven strategies.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Pandemic Containment is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation. Regular assessments of strategies, analysis of data, and a willingness to learn from experiences contribute to refining and strengthening containment efforts over time.
Visit The Healthy Consumer to explore comprehensive resources and support for understanding and participating in effective Pandemic Containment Strategies. Together, let’s build a resilient global defense against health crises.
Mitigating Global Risks: Strategies for Pandemic Preparedness
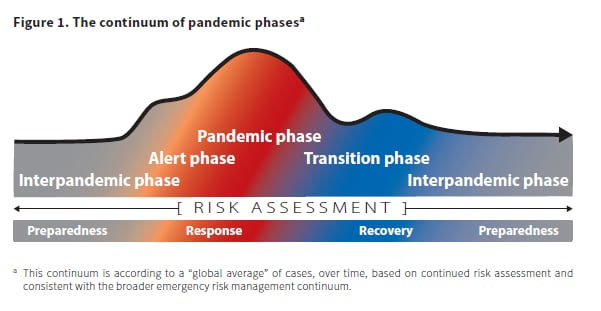
Strategies for Comprehensive Global Pandemic Risk Mitigation
The complexity of global pandemics necessitates proactive and comprehensive risk mitigation strategies. In this article, we explore key approaches to mitigate the risks associated with pandemics on a global scale, fostering resilience and preparedness.
Understanding the Global Nature of Pandemic Risks
Pandemics pose unique challenges due to their global nature. This section delves into the characteristics that make pandemics different from localized crises, emphasizing the need for a coordinated and global approach to effectively mitigate the associated risks.
Early Warning Systems and Surveillance
One of the pillars of global pandemic risk mitigation is the establishment of robust early warning systems. This part of the article discusses the importance of surveillance mechanisms, data analytics, and international cooperation in detecting and responding to potential pandemic threats at an early stage.
International Collaboration and Information Sharing
Mitigating global pandemic risks requires collaboration across borders. This section explores the significance of international cooperation and information sharing among nations, organizations, and public health agencies. Shared data and insights contribute to a more effective global response.
Healthcare Infrastructure Strengthening
Strengthening healthcare infrastructure globally is pivotal for effective risk mitigation. This part of the article discusses strategies for enhancing healthcare systems, including investing in medical facilities, training healthcare professionals, and ensuring access to essential medical supplies.
Vaccine Development and Distribution Strategies
The development and distribution of vaccines play a crucial role in pandemic risk mitigation. This section explores strategies for expediting vaccine development, ensuring equitable distribution, and fostering international collaboration to address global immunization challenges.
Public Health Education and Communication
Educating the public is key to mitigating the impact of a pandemic. This part of the article discusses the importance of public health education and communication campaigns. Clear, consistent, and accessible information empowers individuals to take preventive measures and make informed decisions.
Infrastructure for Remote Work and Learning
The pandemic has highlighted the need for resilient infrastructure to support remote work and learning. This section explores strategies for developing and enhancing digital infrastructure, ensuring that individuals can continue essential activities even during a global health crisis.
Economic Resilience and Financial Preparedness
Mitigating global pandemic risks extends to economic resilience. This part of the article discusses strategies for financial preparedness, including establishing emergency funds, implementing economic stimulus measures, and fostering international collaboration to address the economic fallout of pandemics.
Social Support Systems and Community Resilience
Communities play a vital role in pandemic risk mitigation. This section explores the importance of social support systems, community engagement, and building resilience at the local level. Empowered communities contribute to a more coordinated and effective global response.
TheHealthyConsumer.com: A Hub for Global Pandemic Risk Insights
For in-depth insights into global pandemic risk mitigation, visit TheHealthyConsumer.com. The website offers articles, tips, and resources dedicated to understanding and navigating the complexities of pandemic risk on a global scale.
Looking Ahead: Building a Resilient Global Future
In conclusion, global pandemic risk mitigation requires foresight, collaboration, and a commitment to building resilience. This concluding section reflects on the importance of learning from past experiences, adapting strategies, and continuously working towards a more resilient and prepared global future.
In summary, mitigating global pandemic risks involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses early warning systems, international collaboration, healthcare strengthening, and community resilience. TheHealthyConsumer.com serves as a valuable resource for those seeking guidance on understanding and contributing to the ongoing efforts of global pandemic risk mitigation.




(501).jpg)

