Critical Hubs: Testing Centers in Pandemic Response

Critical Hubs: Testing Centers in Pandemic Response
As the world grapples with the challenges of the ongoing pandemic, testing centers have emerged as critical hubs in the collective response. This article explores the pivotal role of testing centers in pandemic response, delving into their significance, challenges faced, and the broader impact they have on public health and containment efforts.
Testing Centers Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on testing centers during the pandemic, visit Testing Centers Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Rapid Detection and Early Intervention:
Testing centers serve as frontline facilities for rapid detection of COVID-19 cases, enabling early intervention to mitigate the spread of the virus. Timely testing allows for prompt isolation of individuals who test positive, reducing the risk of transmission within communities and facilitating targeted containment strategies.
Diverse Testing Modalities:
Testing centers offer a range of testing modalities to cater to diverse needs. This includes PCR tests for accurate diagnosis, rapid antigen tests for quick results, and antibody tests to assess previous exposure. The availability of various testing options allows for a flexible and comprehensive approach to pandemic testing.
Community Accessibility and Outreach:
Ensuring community accessibility to testing centers is crucial for widespread testing coverage. Testing facilities are strategically located in communities, offering accessible and convenient locations for individuals to get tested. Outreach efforts, including mobile testing units and pop-up testing sites, further enhance accessibility, reaching underserved populations.
Challenges and Solutions in Testing Logistics:
Despite their critical role, testing centers face logistical challenges such as supply chain disruptions, testing kit shortages, and the need for efficient sample processing. This section explores the challenges encountered by testing centers and the innovative solutions implemented to overcome these hurdles, ensuring uninterrupted testing operations.
Drive-Through and Walk-In Testing Formats:
To enhance accessibility and accommodate different preferences, testing centers often adopt diverse testing formats. Drive-through testing centers allow individuals to get tested without leaving their vehicles, providing a convenient and socially distant option. Simultaneously, walk-in testing sites cater to those who prefer on-site testing without the need for vehicle access.
Integration with Contact Tracing Initiatives:
Testing centers play a vital role in integrating with contact tracing initiatives. By identifying and notifying individuals who may have been exposed to the virus, testing results contribute to a comprehensive approach in controlling the spread. The seamless collaboration between testing centers and contact tracing enhances the effectiveness of containment strategies.
Public Awareness and Education:
Testing centers actively contribute to public awareness and education regarding testing protocols and the importance of getting tested. This involves disseminating clear information about testing eligibility, procedures, and the significance of regular testing, fostering a sense of community responsibility in controlling the pandemic.
Technological Innovations in Testing:
Technological innovations have played a significant role in enhancing testing capabilities. This includes the development of rapid testing technologies, online appointment systems, and digital platforms for result notifications. These innovations streamline the testing process, improve efficiency, and contribute to a more seamless testing experience for individuals.
Global Collaboration and Data Sharing:
Testing centers operate within the broader context of global collaboration and data sharing. This section explores how testing centers contribute to international efforts by sharing data, research findings, and best practices. The collective exchange of information facilitates a more informed and coordinated global response to the pandemic.
Conclusion:
In the intricate tapestry of pandemic response, testing centers emerge as critical hubs, facilitating early detection, community accessibility, and integration with broader containment strategies. Despite facing logistical challenges, these centers continue to adapt, innovate, and contribute significantly to public health efforts. As the world navigates the complexities of the ongoing pandemic, the role of testing centers remains pivotal in safeguarding communities and paving the way towards a more resilient and informed future.
Virtual Healing: Telehealth Triumphs in the Pandemic
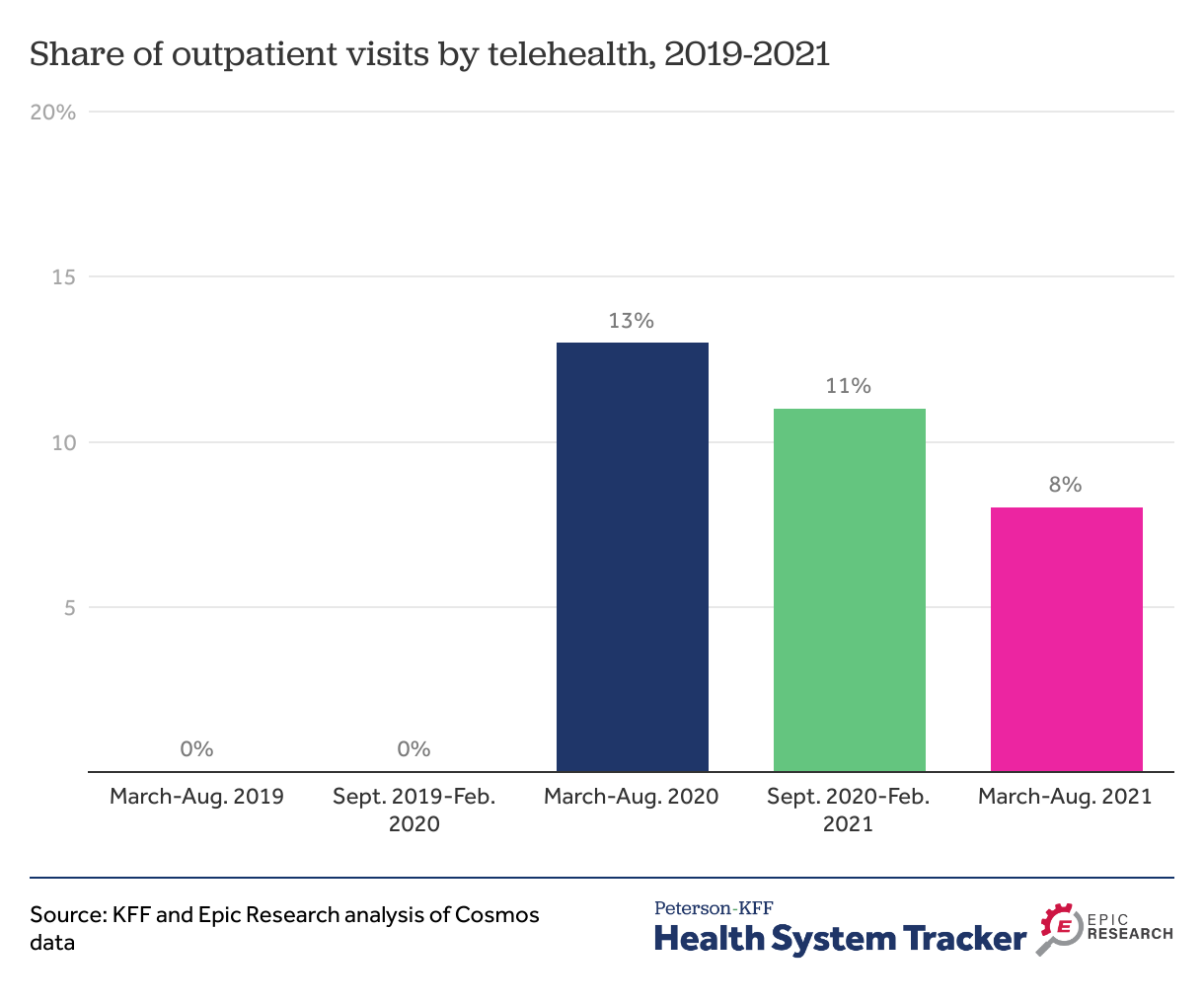
Virtual Healing: Telehealth Triumphs in the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the landscape of healthcare, with telehealth emerging as a transformative solution. This article explores the significant role telehealth has played during the pandemic, its benefits, challenges, and the enduring impact it has on the future of healthcare.
Telehealth During Pandemic: A Comprehensive Guide
For a comprehensive guide on telehealth during the pandemic, visit Telehealth During Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Rise of Telehealth Services:
The pandemic catalyzed the rapid adoption of telehealth services as a means to provide medical care while minimizing physical contact. This section delves into the exponential rise of telehealth platforms, connecting patients with healthcare providers through virtual channels such as video calls, phone consultations, and secure messaging.
Benefits of Telehealth in Pandemic Response:
Telehealth brought forth a myriad of benefits in the pandemic response. This paragraph explores how it enabled timely access to medical advice, reduced the risk of viral transmission in healthcare settings, and provided a lifeline for patients, especially those with chronic conditions, ensuring continuity of care from the safety of their homes.
Expanded Reach and Accessibility:
One notable advantage of telehealth is its ability to overcome geographical barriers. This section discusses how telehealth expanded healthcare accessibility, reaching individuals in remote or underserved areas who might have faced challenges in accessing traditional in-person healthcare services.
Remote Monitoring and Chronic Care Management:
Telehealth proved instrumental in remote monitoring and managing chronic conditions. This paragraph explores how healthcare providers utilized connected devices and wearables to monitor patients’ vital signs, manage chronic diseases, and provide personalized care plans without the need for frequent in-person visits.
Challenges and Solutions in Telehealth Implementation:
Despite its benefits, telehealth faced challenges, including technological barriers, privacy concerns, and the need for regulatory adjustments. This section discusses how healthcare providers and policymakers addressed these challenges through improved technology, enhanced security measures, and streamlined regulations to ensure safe and effective telehealth services.
Telehealth’s Role in Mental Health Support:
The pandemic heightened the need for mental health support, and telehealth emerged as a crucial avenue. This paragraph explores how virtual consultations and therapy sessions provided individuals with access to mental health professionals, reducing stigma, and ensuring ongoing mental health care during challenging times.
Technological Innovations and Integration:
Telehealth spurred technological innovations and integrations in healthcare delivery. This section discusses how artificial intelligence, data analytics, and other technological advancements were integrated into telehealth platforms, enhancing diagnostic capabilities, improving treatment plans, and fostering a more holistic approach to healthcare.
Patient Satisfaction and Quality of Care:
Feedback from patients highlighted high satisfaction levels with telehealth services. This paragraph explores patient experiences, emphasizing the convenience, reduced waiting times, and the positive impact on overall healthcare experiences that telehealth brought to the forefront.
The Future Landscape of Telehealth:
As the pandemic recedes, the impact of telehealth remains significant. This section explores how telehealth has become an integral part of the future healthcare landscape, with hybrid models combining virtual and in-person care likely to persist, offering patients greater flexibility and choice.
Collaboration and Continued Advancements:
The success of telehealth during the pandemic stems from collaborative efforts and ongoing advancements. This paragraph discusses the importance of continued collaboration between healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers to further refine telehealth solutions and ensure its seamless integration into the evolving healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion:
Telehealth has proven to be a transformative force in healthcare, particularly during the challenges posed by the pandemic. From expanding accessibility to providing remote monitoring and mental health support, its benefits are vast. As we look ahead, the lessons learned from the pandemic underscore the enduring role of telehealth in shaping a more resilient, accessible, and patient-centered healthcare system.
Unraveling Global Pandemic Trends: Insights and Impact
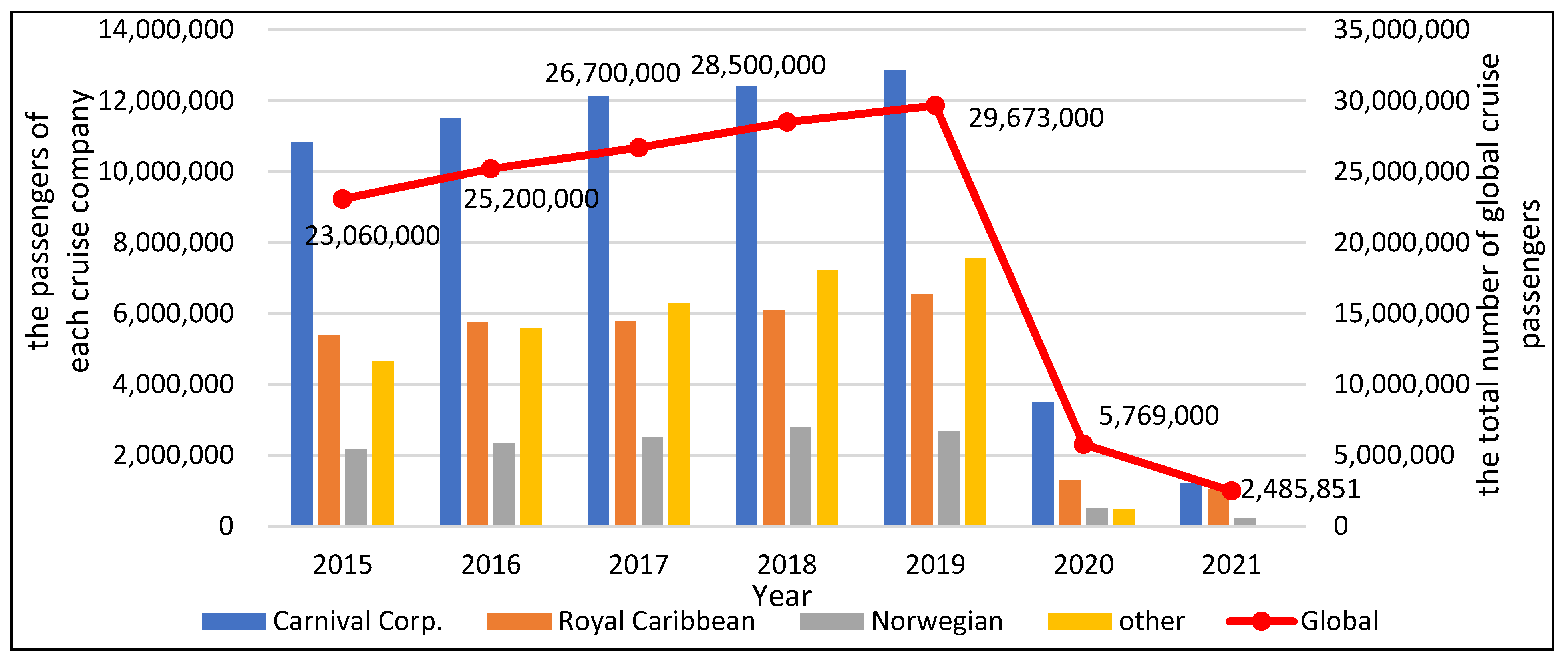
Unraveling Global Pandemic Trends: Insights and Impact
The global landscape has been significantly shaped by the ebb and flow of the ongoing pandemic. Examining and understanding Global Pandemic Trends provides crucial insights into the multifaceted impact on societies, economies, and public health.
Analyzing the Dynamics of Spread
One key aspect of Global Pandemic Trends is the analysis of how infectious diseases spread across regions. Studying transmission patterns, hotspots, and factors influencing the virus’s movement helps in formulating targeted strategies for containment and mitigation.
Economic Fluctuations and Adaptations
Global Pandemic Trends have triggered economic fluctuations on an unprecedented scale. Industries, businesses, and job markets experience shifts in response to lockdowns, remote work trends, and changes in consumer behavior. Understanding these economic dynamics is essential for recovery planning.
Healthcare Infrastructure Resilience
The pandemic has underscored the importance of resilient healthcare infrastructure. Examining Global Pandemic Trends in healthcare reveals the strengths and weaknesses of systems worldwide. Insights gained contribute to bolstering healthcare preparedness for future health crises.
Technological Innovations in Response
Global Pandemic Trends have accelerated the adoption of technology in various sectors. From telemedicine to remote work solutions, technological innovations have played a crucial role in response efforts. Analyzing these trends sheds light on the future integration of technology in healthcare and work environments.
Shifts in Public Health Priorities
The pandemic has prompted a reevaluation of public health priorities globally. Global Pandemic Trends reflect shifts in focus, with increased attention on infectious disease preparedness, vaccination infrastructure, and mental health support.
Education Transformations and Challenges
The education sector has undergone significant transformations in response to Global Pandemic Trends. Remote learning, digital classrooms, and hybrid models have become commonplace. Examining these trends informs ongoing discussions about the future of education.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Global Pandemic Trends extend beyond health and economics to influence social and cultural norms. Changes in social interactions, attitudes toward public health measures, and the redefinition of cultural practices are all part of the evolving landscape.
Environmental Considerations
The pandemic has prompted reflections on the environmental impact of human activities. Global Pandemic Trends include shifts in pollution levels, changes in travel patterns, and discussions on sustainable practices. These trends contribute to ongoing dialogues about environmental conservation.
Community Resilience and Solidarity
Examining Global Pandemic Trends also unveils stories of community resilience and solidarity. Individuals and communities worldwide have come together to support one another. Understanding these trends fosters a sense of shared experience and collective strength.
Navigating the Future – Global Pandemic Trends
In navigating the future, it’s essential to stay informed about Global Pandemic Trends. The Healthy Consumer serves as a valuable resource, offering insights, resources, and support for understanding and adapting to the evolving global landscape. Explore the trends, gain knowledge, and actively participate in shaping a resilient future.
Strategic Pandemic Containment: Effective Global Approaches

Strategic Pandemic Containment: Effective Global Approaches
In the ongoing battle against global health crises, understanding and implementing effective Pandemic Containment Strategies are paramount. This article delves into the multifaceted approaches that contribute to successfully containing pandemics on a global scale.
Early Detection and Surveillance
Pandemic Containment begins with early detection and robust surveillance systems. Identifying and monitoring potential outbreaks allow for swift responses, enabling authorities to implement containment measures before the situation escalates. Surveillance is a cornerstone in preventing the rapid spread of infectious diseases.
Strategic Testing and Contact Tracing
Strategic testing and contact tracing are integral components of Pandemic Containment Strategies. Widely available testing, combined with efficient contact tracing, helps identify and isolate infected individuals promptly. This proactive approach disrupts the chain of transmission and limits the spread of the virus.
Quarantine and Isolation Protocols
Implementing effective quarantine and isolation protocols is crucial in controlling the spread of a pandemic. By isolating infected individuals and quarantining those exposed, authorities can minimize the risk of widespread transmission. Clear guidelines and communication are essential for public adherence to these protocols.
Vaccination Campaigns and Immunization
A cornerstone in Pandemic Containment is widespread vaccination. Vaccination campaigns contribute to achieving population immunity, reducing the severity of illness, and preventing further spread. Ensuring equitable access to vaccines globally is essential for comprehensive and effective containment.
Public Health Education and Communication
Transparent and accessible communication is vital in Pandemic Containment. Public health education campaigns inform the public about the virus, preventive measures, and the importance of cooperation. Clear and consistent messaging fosters a sense of shared responsibility and encourages adherence to guidelines.
Global Cooperation and Data Sharing
Global cooperation is indispensable in Pandemic Containment. Countries and organizations must share information, resources, and expertise. Collaborative efforts enhance the collective response, allowing for a more unified approach to challenges such as vaccine distribution, research, and containment strategies.
Adaptive Policy Implementation
Flexibility in policy implementation is key in dynamic situations. Governments and health authorities must adapt Pandemic Containment Strategies based on evolving circumstances. This adaptability ensures that responses remain effective in addressing the unique challenges posed by each phase of a pandemic.
Community Engagement and Support
Pandemic Containment is more effective when communities actively participate. Engaging the public through community outreach programs, addressing concerns, and providing support fosters a sense of shared responsibility. Communities become active partners in the fight against the pandemic.
Technological Innovations in Containment
Technological innovations play a pivotal role in Pandemic Containment. From contact tracing apps to data analytics, technology enhances the efficiency of containment efforts. Embracing and continually improving these innovations contribute to more effective and data-driven strategies.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Pandemic Containment is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation. Regular assessments of strategies, analysis of data, and a willingness to learn from experiences contribute to refining and strengthening containment efforts over time.
Visit The Healthy Consumer to explore comprehensive resources and support for understanding and participating in effective Pandemic Containment Strategies. Together, let’s build a resilient global defense against health crises.
Revolutionizing Healthcare: Telehealth Solutions Amid Pandemic
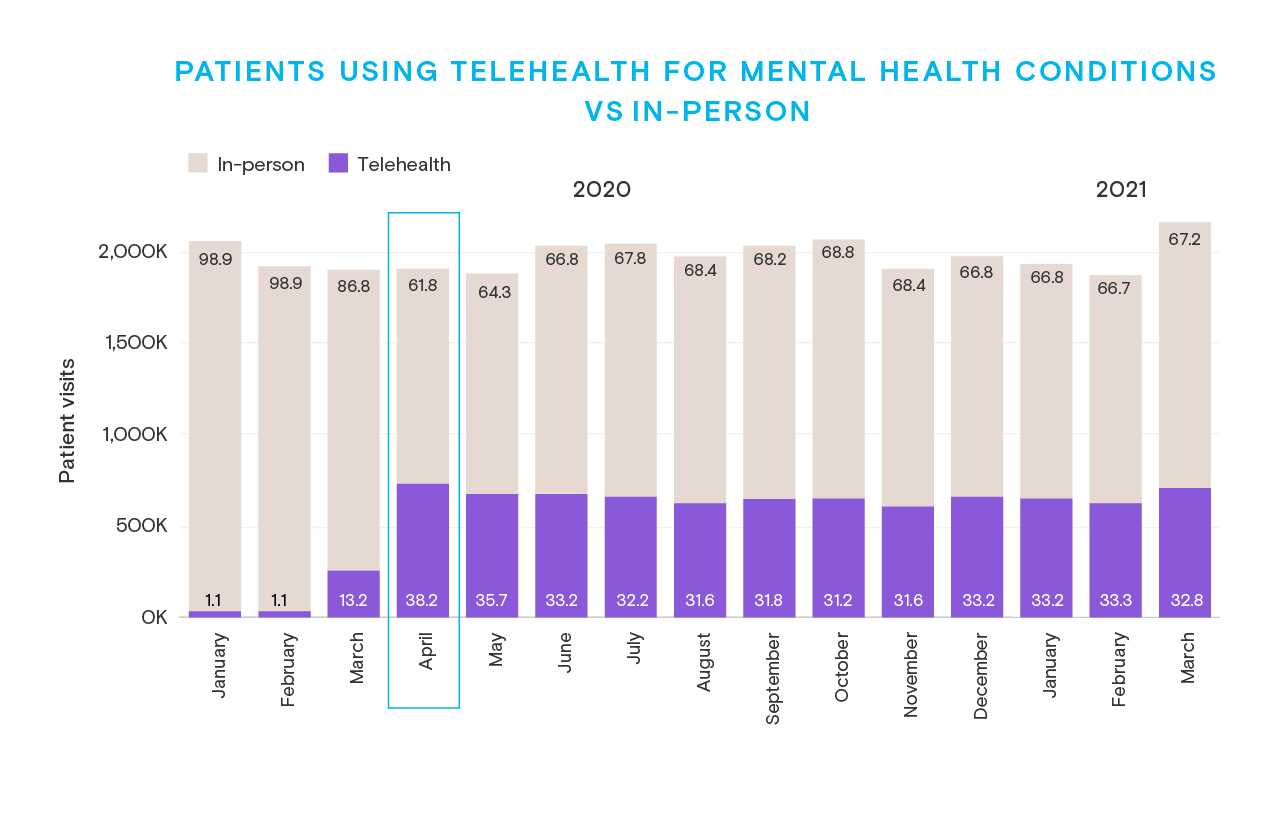
The Evolution of Healthcare: Telehealth Solutions Amid Pandemic Challenges
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telehealth solutions, revolutionizing the way healthcare services are delivered. As the world navigates through unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a critical tool, offering innovative solutions to ensure the continuity and accessibility of healthcare services.
Rise of Telehealth during the Pandemic:
The pandemic prompted a rapid shift towards telehealth solutions, driven by the need to provide medical care while minimizing in-person interactions. Telehealth encompasses a range of services, including virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and digital communication tools. This surge in telehealth adoption has not only addressed immediate concerns but has also set the stage for a transformative future in healthcare delivery.
Accessibility and Overcoming Geographic Barriers:
One of the key advantages of telehealth is its ability to overcome geographic barriers. Patients in remote or underserved areas can now access healthcare services without the need for extensive travel. Telehealth solutions have brought medical expertise to the fingertips of individuals, fostering a more inclusive and accessible healthcare system.
Virtual Consultations and Remote Monitoring:
Telehealth solutions have redefined the patient-doctor relationship with the widespread adoption of virtual consultations. Patients can seek medical advice, discuss symptoms, and receive prescriptions from the comfort of their homes. Remote monitoring tools enable healthcare professionals to track patients’ vital signs and chronic conditions, allowing for timely interventions and personalized care plans.
Enhanced Healthcare Efficiency:
The integration of telehealth solutions has streamlined healthcare processes, leading to increased efficiency. Digital health records, virtual appointments, and online prescription services have reduced administrative burdens, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care. This efficiency not only benefits healthcare professionals but also contributes to a more responsive and patient-centric healthcare system.
Telehealth Solutions Pandemic: Transforming Patient Experience
To explore the transformative impact of telehealth solutions during the pandemic, visit Telehealth Solutions Pandemic for valuable insights and resources.
Technological Innovations in Telehealth:
Advancements in technology have played a crucial role in the evolution of telehealth solutions. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), wearable devices, and telemedicine apps has enhanced the diagnostic capabilities and personalized treatment options. These technological innovations contribute to a more comprehensive and proactive approach to healthcare.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations:
While telehealth solutions offer numerous benefits, they also come with challenges and regulatory considerations. Issues such as data security, licensure requirements, and reimbursement policies need careful attention. Addressing these challenges is essential to ensure the widespread and sustainable integration of telehealth into the broader healthcare landscape.
Patient Empowerment and Health Literacy:
Telehealth empowers patients by providing them with greater control over their healthcare journey. Increased health literacy, facilitated by access to information and virtual resources, enables individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being. Telehealth solutions contribute to a paradigm shift, where patients become active participants in their healthcare management.
Sustainable Healthcare for the Future:
As telehealth solutions continue to evolve, they are poised to become an integral part of the future healthcare landscape. The lessons learned during the pandemic highlight the importance of flexible and resilient healthcare systems. Telehealth is not just a temporary response to a crisis but a sustainable solution that can enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and patient outcomes in the long run.
Conclusion:
The integration of telehealth solutions into mainstream healthcare practices marks a significant milestone in the evolution of medical services. From virtual consultations to technological innovations, telehealth has proven its ability to transform patient experiences, enhance healthcare efficiency, and contribute to a more accessible and patient-centric healthcare system. As the world embraces the future of healthcare, telehealth solutions stand as a beacon of innovation and resilience in the face of ongoing challenges.





