Vaccination Rollout: Progress and Strategies Amid Pandemic

Vaccination Rollout: Progress and Strategies Amid Pandemic
The global vaccination rollout stands as a critical milestone in the fight against the pandemic. This article explores the progress made, challenges faced, and strategies employed in the ongoing vaccination efforts worldwide.
Global Vaccination Progress
The global vaccination effort has witnessed remarkable progress since the introduction of COVID-19 vaccines. Countries around the world have initiated mass vaccination campaigns to immunize their populations against the virus. The speed at which vaccines have been developed and deployed underscores the urgency of curbing the spread of the virus.
Challenges in Distribution and Accessibility
Despite progress, challenges in vaccine distribution and accessibility persist. Many regions face hurdles in securing an adequate supply of vaccines, and logistical challenges can hinder the efficient delivery of doses. Ensuring equitable access to vaccines remains a crucial aspect of the global vaccination strategy.
Variants and the Need for Flexibility
The emergence of new virus variants adds complexity to the vaccination rollout. Adapting vaccine strategies to address these variants requires flexibility and ongoing research. Vaccine developers and health authorities continually monitor and adjust vaccination approaches to maintain effectiveness against evolving strains of the virus.
Public Communication and Vaccine Hesitancy
Effective communication is essential in encouraging widespread vaccine acceptance. However, vaccine hesitancy poses a challenge, with misinformation and concerns impacting public perception. Public health authorities work to address misconceptions, provide accurate information, and build trust to enhance vaccine uptake.
Vaccination Strategies for Vulnerable Populations
Protecting vulnerable populations is a key focus of vaccination strategies. This includes prioritizing older adults, individuals with underlying health conditions, and those in congregate settings. Tailoring vaccination approaches to meet the unique needs of these groups is critical for reducing severe illness and mortality.
Global Cooperation and Vaccine Diplomacy
Global cooperation plays a pivotal role in ensuring the success of the vaccination rollout. Countries, organizations, and pharmaceutical companies collaborate to share resources, knowledge, and vaccine doses. Vaccine diplomacy efforts aim to address global disparities in vaccine access and distribution.
Addressing Supply Chain Challenges
The vaccine rollout has highlighted the importance of resilient supply chains. Challenges in the production, distribution, and storage of vaccines underscore the need for strategic planning and international collaboration to overcome supply chain hurdles and ensure a steady flow of doses.
Integration of Technology in Vaccination Management
Technology plays a vital role in streamlining vaccination processes. Digital tools, such as appointment scheduling systems and vaccine passports, contribute to efficient and organized vaccination campaigns. Leveraging technology enhances data management, tracking, and communication throughout the vaccination rollout.
Booster Dose Considerations
As vaccination efforts progress, discussions around booster doses come to the forefront. Evaluating the need for booster shots to enhance immunity and address emerging variants is an ongoing aspect of vaccination strategy. Health authorities weigh scientific evidence and global trends to determine the optimal approach.
The Path Forward: Achieving Herd Immunity
The ultimate goal of the vaccination rollout is to achieve herd immunity, limiting the spread of the virus within communities. This requires a significant percentage of the population to be vaccinated. Continued efforts in outreach, education, and accessibility are essential for reaching this critical milestone.
Visit The Healthy Consumer for comprehensive information and resources on the ongoing vaccination rollout. Together, let’s contribute to the collective effort in overcoming the challenges posed by the pandemic through vaccination.
Adapting to Remote Work: Strategies Amidst the Pandemic

Adapting to Remote Work: Strategies Amidst the Pandemic
The global pandemic has transformed the way we work, with remote work becoming a prevalent and necessary adaptation. In this article, we explore the strategies and considerations for effectively navigating the challenges and seizing the opportunities presented by remote work during these unprecedented times.
The Acceleration of Remote Work Trends
The pandemic acted as a catalyst for remote work trends, accelerating the adoption of flexible work arrangements. This section delves into the factors contributing to this acceleration, including the need for social distancing, advancements in technology, and the prioritization of employee safety and well-being.
Implementing Technology for Seamless Collaboration
Technology is the linchpin of successful remote work. This part of the article discusses the critical role of collaborative tools, video conferencing platforms, project management software, and cloud-based solutions in facilitating seamless communication and collaboration among remote teams.
Establishing Clear Remote Work Policies
Clear and comprehensive policies are fundamental when adapting to remote work. This section explores the importance of establishing remote work policies that outline expectations, communication protocols, and guidelines for maintaining productivity while fostering work-life balance.
Prioritizing Employee Well-being and Engagement
Employee well-being takes center stage in remote work adaptations. This part of the article delves into strategies for prioritizing the mental and emotional health of remote employees, including regular check-ins, virtual team-building activities, and initiatives that promote a sense of connection and belonging.
Balancing Flexibility with Accountability
Balancing flexibility with accountability is a delicate but crucial aspect of remote work. This section explores how organizations can strike the right balance, allowing flexibility in work hours and location while maintaining accountability through clear performance expectations and measurable outcomes.
Addressing Remote Security Concerns
As remote work expands, so do security concerns. This part of the article discusses strategies for addressing cybersecurity and data protection issues associated with remote work. Implementing secure networks, training employees on cybersecurity best practices, and employing encryption measures are essential steps.
Promoting Inclusivity and Diversity in Remote Settings
Remote work environments should prioritize inclusivity and diversity. This section explores how organizations can ensure that remote work arrangements do not inadvertently lead to disparities. Initiatives such as diverse hiring practices, accessibility considerations, and cultural sensitivity training contribute to an inclusive remote culture.
Investing in Employee Skill Development
Remote work often necessitates new skill sets. This part of the article discusses the importance of investing in employee skill development, including training programs, upskilling initiatives, and continuous learning opportunities to empower employees to thrive in the digital work landscape.
TheHealthyConsumer.com: Your Guide to Remote Work Adaptations
For in-depth insights into remote work adaptations during the pandemic, visit TheHealthyConsumer.com. The website offers articles, tips, and resources dedicated to understanding and navigating the complexities of remote work in these challenging times.
Looking Ahead: Remote Work as the New Normal
In conclusion, remote work adaptations during the pandemic are not merely a temporary measure but a transformative shift in the way we work. This concluding section reflects on the enduring impact of remote work and the need for continued adaptation and innovation in the evolving work landscape.
In summary, adapting to remote work involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing technology integration, policy development, employee well-being, and a commitment to inclusivity. TheHealthyConsumer.com serves as a valuable resource for those seeking guidance on understanding and contributing to the ongoing efforts of remote work adaptations in these unprecedented times.
Navigating Crisis: Effective Management During the Pandemic
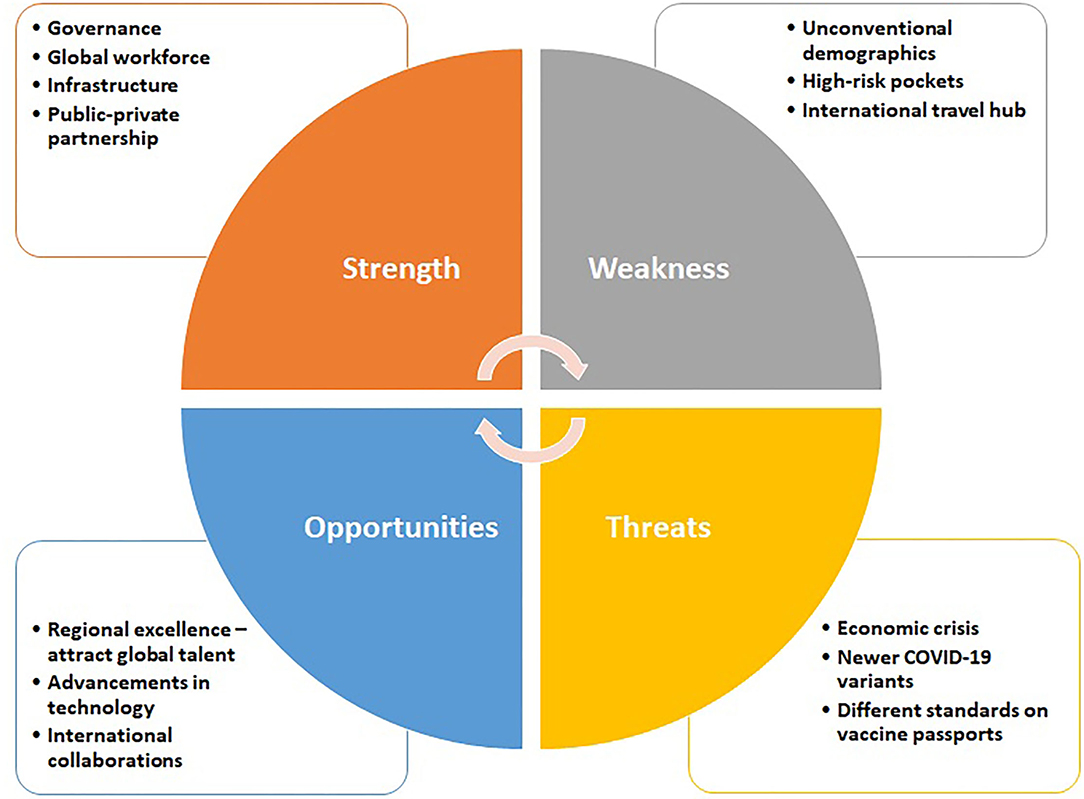
The Imperative of Pandemic Crisis Management
In the face of a global pandemic, effective crisis management is paramount to navigate uncertainties and mitigate the impact on individuals, communities, and organizations. This article explores the essential components and strategies for adeptly managing crises during these challenging times.
Understanding the Dynamic Nature of Pandemic Crises
Pandemic crises are dynamic and multifaceted, requiring a nuanced understanding of their evolving nature. From public health challenges to economic disruptions and social impacts, crisis management must encompass a comprehensive perspective to address the diverse aspects of the crisis.
Developing a Robust Crisis Response Plan
A foundational element of pandemic crisis management is the development of a robust response plan. This plan should outline clear roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, resource allocation strategies, and contingency measures. A well-prepared response plan forms the basis for swift and coordinated actions in times of crisis.
Effective Communication: A Cornerstone of Crisis Management
Communication is central to crisis management, particularly during a pandemic. Timely, transparent, and accurate communication builds trust and ensures that individuals and stakeholders are well-informed. The dissemination of vital information about safety measures, updates, and support resources is crucial for effective crisis response.
Coordination and Collaboration Across Sectors
Pandemic crises necessitate collaboration across various sectors, including healthcare, government, businesses, and communities. Coordinated efforts enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of crisis management. Partnerships between public and private entities, as well as international collaboration, contribute to a more resilient response.
Prioritizing Public Health and Safety Measures
Protecting public health and safety is paramount in pandemic crisis management. Implementing and enforcing measures such as social distancing, testing, contact tracing, and vaccination campaigns are critical components. Prioritizing these measures contributes not only to immediate crisis response but also to long-term resilience.
Addressing Economic Impact Through Strategic Measures
The economic fallout from a pandemic requires strategic measures to alleviate its impact. Governments and organizations may implement stimulus packages, financial support, and economic recovery plans. Balancing the economic considerations with public health priorities is essential for comprehensive crisis management.
Supporting Vulnerable Populations and Communities
Vulnerable populations often bear a disproportionate burden during crises. Crisis management strategies must include targeted support for these communities, addressing their specific needs and challenges. This includes access to healthcare, economic assistance, and social services tailored to vulnerable demographics.
Adapting Technology for Crisis Response
The integration of technology plays a pivotal role in crisis response. From data analytics for informed decision-making to the use of digital platforms for communication and coordination, technology enhances the efficiency and reach of crisis management efforts. Embracing innovation is key in navigating a rapidly evolving crisis landscape.
Evaluating and Learning from Crisis Responses
A critical aspect of crisis management is continuous evaluation and learning. After the initial response, assessing the effectiveness of measures, identifying areas for improvement, and incorporating lessons learned into future crisis plans contribute to adaptive and resilient crisis management.
Pandemic Crisis Management: A Collective Responsibility
In the face of a pandemic crisis, the responsibility for effective management extends to individuals, communities, organizations, and governments alike. A collective commitment to adhering to safety measures, supporting one another, and actively participating in crisis response initiatives is pivotal for overcoming challenges.
Explore More about Pandemic Crisis Management
Stay informed about pandemic crisis management strategies and insights at Pandemic Crisis Management. Together, let us navigate these challenging times with resilience, adaptability, and a shared commitment to overcoming crises.
Global Testing Hubs: Navigating the Pandemic Landscape

Setting the Stage: The Role of Global Pandemic Testing Centers
In the relentless battle against a global pandemic, the establishment of robust testing centers worldwide has become instrumental. These centers serve as pivotal hubs for early detection, strategic testing, and the formulation of effective public health responses, collectively contributing to global efforts in navigating the challenging landscape of infectious diseases.
Strategic Placement for Maximum Impact
The strategic placement of global pandemic testing centers is paramount. These centers are strategically located to ensure maximum coverage and accessibility, allowing for swift responses to emerging outbreaks. From urban areas to remote regions, the goal is to create a network that can quickly identify and contain the spread of infectious agents, regardless of geographical boundaries.
Early Detection: The Cornerstone of Effective Response
Global pandemic testing centers play a central role in early detection, acting as the cornerstone of an effective response. By offering accessible and widespread testing, these centers enable authorities to identify cases promptly. Early detection is crucial for implementing timely interventions, isolating individuals, and preventing the further spread of the infectious agent.
Diverse Testing Protocols for Varied Needs
The diversity of testing protocols implemented at global pandemic testing centers caters to varied needs. From PCR tests for accurate diagnosis to rapid antigen tests for quick results, the range of testing methods ensures flexibility in responding to different scenarios. Tailoring testing strategies to the specific characteristics of the infectious agent enhances the effectiveness of containment measures.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Ensuring accessibility and inclusivity is a key aspect of global pandemic testing center initiatives. These centers are designed to be easily accessible to diverse populations, addressing geographical, economic, and social factors. Inclusivity in testing helps identify cases across all segments of society, preventing disparities in healthcare access and promoting a more equitable response.
Technology Integration for Efficiency
Global pandemic testing centers leverage technology for efficiency and accuracy. Automated testing processes, data management systems, and digital communication channels streamline operations. Technology integration enhances the speed of testing, reduces turnaround times for results, and facilitates real-time data sharing, contributing to a more responsive and interconnected global health network.
International Collaboration: Sharing Data and Resources
The essence of global pandemic testing centers lies in international collaboration. These centers function as hubs for the exchange of data, resources, and expertise on a global scale. Collaborative efforts strengthen the collective response, allowing nations to learn from each other’s experiences, share best practices, and harmonize strategies for effective pandemic management.
Training and Capacity Building
Global pandemic testing centers prioritize training and capacity building. Ensuring that healthcare professionals are well-equipped to conduct tests, interpret results, and adhere to safety protocols is crucial. Capacity building initiatives contribute to the proficiency of testing procedures, fostering a standardized and high-quality approach across different testing centers.
Surveillance and Monitoring for Emerging Threats
Beyond routine testing, global pandemic testing centers are instrumental in surveillance and monitoring for emerging threats. The continuous surveillance of infectious agents allows for the early detection of potential outbreaks and the swift implementation of containment measures. Vigilance is maintained to stay ahead of evolving pathogens and prevent widespread transmission.
Public Awareness and Trust-Building
Global pandemic testing centers actively engage in public awareness campaigns and trust-building initiatives. Transparent communication about the importance of testing, the confidentiality of data, and the role of testing in public health contributes to community understanding and cooperation. Building trust is essential for fostering widespread acceptance and participation in testing efforts.
To delve deeper into the role of global pandemic testing centers, visit Global Pandemic Testing Centers. As the world collectively faces the challenges posed by infectious diseases, the strategic placement, early detection capabilities, and collaborative nature of these testing centers become pivotal in the ongoing efforts to safeguard global health.
Adapting Education: Remote Learning Strategies Amid Pandemic

Adapting Education: Remote Learning Strategies Amid Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped education, prompting a surge in remote learning. In this article, we explore effective strategies for adapting to the challenges posed by the pandemic and ensuring the success of remote learning initiatives.
Technology Integration: The Backbone of Remote Learning
Integrating technology into education has become paramount in the era of remote learning. Platforms such as video conferencing, online collaboration tools, and learning management systems facilitate seamless communication and interaction between students and educators. Embracing technology is the first step in creating a dynamic and engaging remote learning environment.
Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning: Balancing Flexibility and Interaction
Remote learning allows for a blend of synchronous and asynchronous learning experiences. Synchronous sessions, conducted in real-time, offer opportunities for live interactions, discussions, and immediate feedback. Asynchronous learning, on the other hand, provides flexibility by allowing students to access materials and complete tasks at their own pace. Striking a balance between these approaches accommodates diverse learning preferences.
Engagement Strategies: Fostering Active Participation
Maintaining student engagement is a challenge in remote learning environments. Educators employ various strategies, such as interactive quizzes, polls, and virtual group activities, to foster active participation. Creating a sense of community through online forums and discussion boards also enhances student engagement and contributes to a more enriching learning experience.
Clear Communication: Building Transparent Connections
Clear communication is fundamental in remote learning. Educators must articulate expectations, assignment details, and communication protocols clearly. Regular updates on schedules, assessments, and any changes in the course structure build transparent connections between educators and students. Effective communication minimizes confusion and ensures everyone is on the same page.
Flexible Assessments: Adapting Evaluation Methods
Traditional assessment methods may need modification in a remote learning setting. Implementing a variety of assessment tools, such as online quizzes, written assignments, and project submissions, accommodates different learning styles. Flexibility in assessment methods ensures that students can demonstrate their understanding in ways that suit their strengths.
Professional Development for Educators: Enhancing Digital Literacy
Educators play a crucial role in the success of remote learning. Providing professional development opportunities to enhance digital literacy and teaching skills is essential. Training programs on effective online instruction, technology usage, and adapting curriculum for remote environments empower educators to deliver high-quality education.
Equitable Access to Resources: Addressing Disparities
Ensuring equitable access to resources is a priority in remote learning. Schools must consider the varying levels of access to technology and the internet among students. Implementing solutions, such as providing devices or internet connectivity assistance to those in need, helps address disparities and ensures that all students can fully participate in remote learning.
Supporting Student Well-being: Prioritizing Mental Health
The shift to remote learning can impact student well-being. Educators and institutions must prioritize mental health by creating a supportive environment. This includes fostering open communication, providing resources for stress management, and recognizing the challenges students may face in adapting to remote learning.
Parental Involvement: Collaborating for Success
Remote learning requires collaboration between educators and parents. Keeping parents informed about the curriculum, expectations, and providing guidance on supporting their children’s learning at home fosters a collaborative approach. Regular communication channels, such as virtual parent-teacher meetings, strengthen the partnership between home and school.
Accessing Remote Learning Strategies Pandemic: A Resource Hub
For additional insights and resources on effective remote learning strategies during the pandemic, consider exploring Remote Learning Strategies Pandemic. This centralized hub provides valuable information, best practices, and support for educators, students, and parents navigating the challenges of remote learning in these unprecedented times.




(501).jpg)

